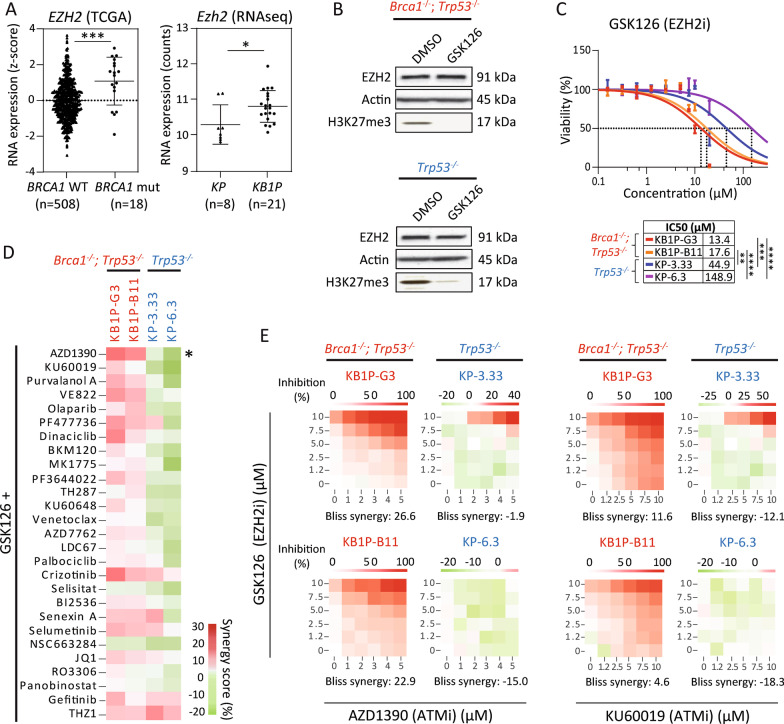
Fig. 1.
Synergistic cytotoxicity screen in combination with GSK126-induced EZH2 inhibition. A Increased EZH2 mRNA expression in BRCA1-deficient breast cancer. Left panel: EZH2 expression using the TCGA breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA) whole-exome sequencing data set (n = 826). Data are shown as z-score transformed in BRCA1-wild type (n = 508) versus BRCA1-mutated (n = 18) breast tumors. Right panel: Ezh2 expression using RNAseq data from BRCA1-proficient KP (n = 8) and BRCA1-deficient KB1P mouse mammary tumors (n = 21). Groups were compared using an unpaired Mann–Whitney U test. B Target inhibition of H3K27me3 after 72 h of GSK126 treatment (5 µM) shown by a representative immunoblot in BRCA1-deficient KB1P-G3 and BRCA1-proficient KP-3.33 cells, β-actin served as loading control. C Single agent dose–response curves and determination of IC50 value of GSK126 in four mouse mammary tumor cell lines. Statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison test. D Heatmap showing synergy scores calculated by the Bliss independence model of 27 compounds in combination with GSK126 across four murine mammary tumor cell lines after 72 h treatment. Combinations are arranged by the difference in synergy score between BRCA1-deficient and BRCA1-proficient cell lines from high to low. Cell lines are arranged by the Brca1 mutation status. Concentrations and IC50 values of single compounds can be found in Additional file 8: Table S1. Asterix indicates the prioritized compound AZD1390. E Heatmaps visualized by the web-application tool SynergyFinder showing synergy scores of treatment combinations GSK126/AZD1390 and GSK126/KU60019, respectively. Displayed colors reflect the growth inhibition in percent with red indicating stronger inhibition and green indicating lower inhibition