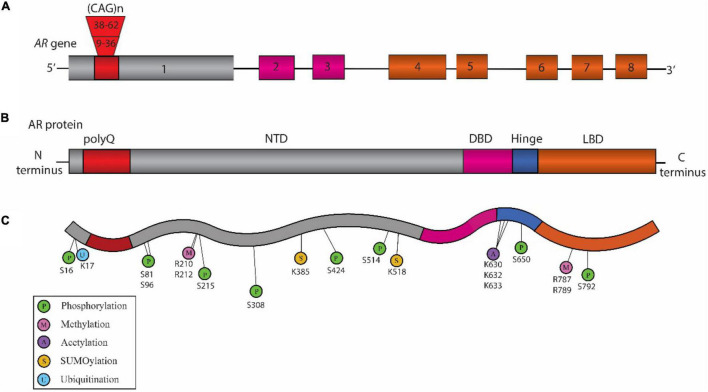
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of the structure of Androgen Receptor (AR) gene, protein, and posttranslational modifications (PTM) sites associated with Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy (SBMA) pathogenesis. (A) Structure of AR gene: The AR gene is located on the X chromosome and is comprised of eight exons. The color-coded exons indicate the major functional domains in the translated AR protein. (B) Domain architecture of AR: Schematic illustration showing the key domains that include the N-terminal domain (NTD, shown in gray), the DNA binding domain (DBD, pink), a short hinge region (blue), and the C-terminal ligand binding domain (LBD, orange) in the AR protein. (C) SBMA-associated PTM sites on the AR: The sites include phosphorylation sites (P, green), methylation sites (M, pink), acetylation sites (A, purple) SUMOylation sites (S, yellow), and ubiquitination sites (U, blue). The position of these PTM sites is indicated below their respective circles.