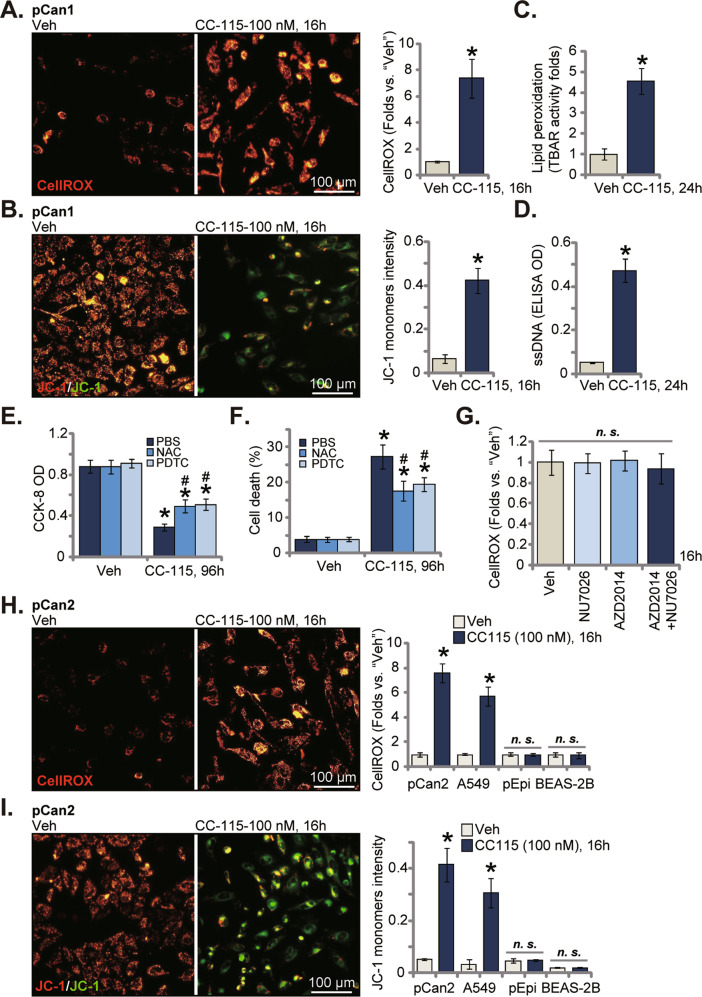
Fig. 5. CC-115 induces ROS production and oxidative injury in NSCLC cells.
The pCan1/pCan2 primary human NSCLC cells, the immortalized A549 NSCLC cells, the primary human lung epithelial cells (“pEpi”) or the BEAS-2B bronchial epithelial cells were treated with CC-115 (100 nM), and cultivated for the designated time periods; ROS production, mitochondrial depolarization, lipid peroxidation and DNA breaks were tested by measuring CellROX intensity A, H, JC-1 green monomers intensity B, I, the TBAR activity C and single strand DNA ELISA intensity D, respectively. pCan1 cells were pretreated for 35 min with n-acetyl cysteine (NAC, 500 μM), pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC, 10 μM) or vehicle control (PBS), followed by CC-115 (100 nM, 96 h) treatment, cell viability E and death F were examined. pCan1 cells were treated with AZD2014 (100 nM), NU7026 (100 nM), or AZD2014 plus NU7026, cells were further cultivated for 16 h; ROS intensity was tested by measuring CellROX intensity G. For each assay, n = 5. *P < 0.05 versus “Veh” group. #P < 0.05 versus “PBS” group E, F. “n.s.” stands for non-statistical difference. Scale bar = 100 μm A, B, H, and I.