Figure 9.
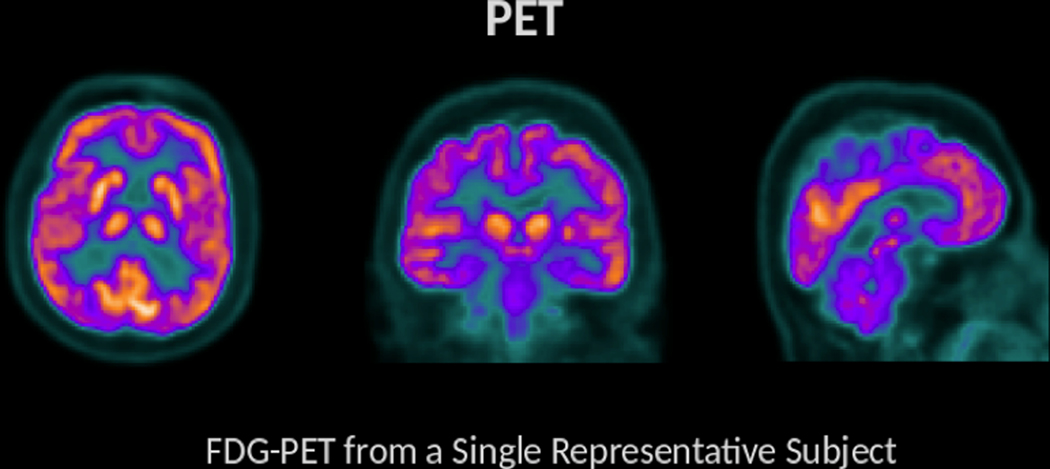
FDG-PET is a procedure that provides information about energy utilization in the brain. This is achieved through the use of an injected radiolabeled analog of glucose (FDG). Given that glucose is a primary energy substrate in the brain, FDG accumulation within brain areas is a marker of metabolic activity and this measure of energetics is regionally diminished in a variety of clinical conditions. Brighter colors are found in regions with greater tracer uptake (and therefore greater metabolic activity).
