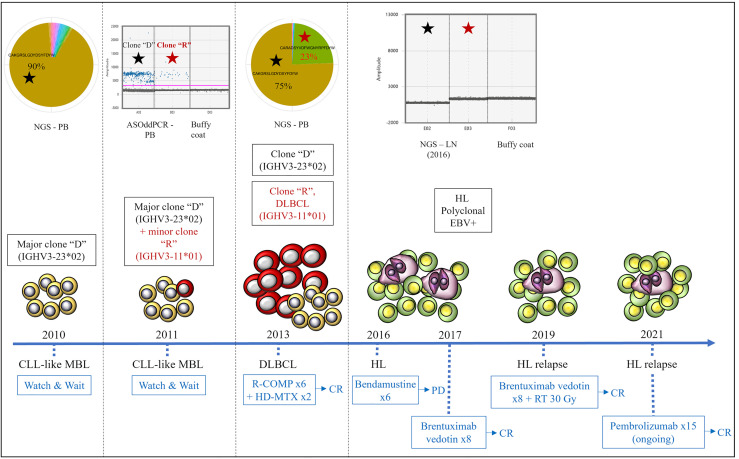
Figure 2.
Clonal relationships by Ig-rep and ASO-ddPCR and clinical evolution of the three lymphoid neoplasms. Clone “D” (indicated with a black star) was detected in the PB sample collected at the time of MBL diagnosis and was persistent in the PB collected at the time of DLBCL. Clone “R” (i.e., the clone identified in the lymph node biopsy at the time of DLBCL transformation, indicated with a red star) was undetectable by NGS of Ig-rep in the PB sample collected at the time of MBL diagnosis, whereas it became detectable by ASO-ddPCR in an interim PB sample collected during the “watch & wait” period (where it coexisted with clone “D”). Neither clone “D” nor clone “R” were detectable in the lymph node specimen collected at the time of HL. ASO-ddPCR, allele-specific oligonucleotide-droplet digital PCR; NGS, next-generation sequencing; Ig-rep, immunoglobulin repertoire; PB, peripheral blood; LN, lymph node; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; HL, Hodgkin’s lymphoma; MBL, monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; R-COMP, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, liposomal doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone; HD-MTX, high-dose methotrexate; CR, complete response; PD, progressive disease; RT, radiotherapy.