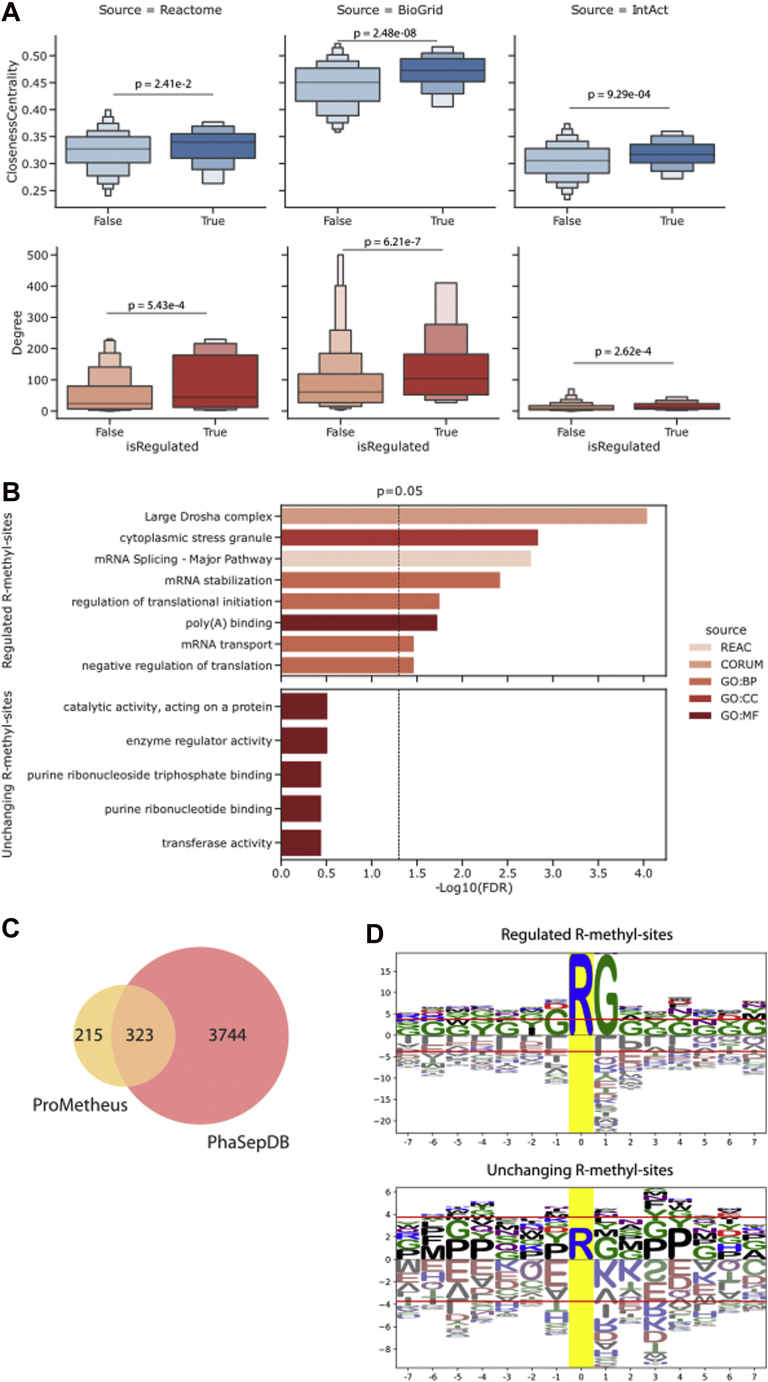
Fig. 4.
Functional analysis of dynamically regulated R methylations.A, topology analysis performed on the Reactome network reveals that proteins bearing at least one significantly regulated R-methyl-site have significantly higher degree and network centrality than those without regulated R-methyl-sites (p values are calculated with Mann–Whitney test). B, functional enrichment performed on proteins bearing at least one regulated R-methyl-site (top) or no regulated R-methyl-sites (bottom). C, intersection of PhaSepDB and ProMetheusDB shows that 60% of R-methyl-proteins are involved in the process of liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS). D, motif analysis performed on significantly regulated (top) and unchanging (bottom) R-sites. Logos were generated using the full list of identified methyl-sites as background.