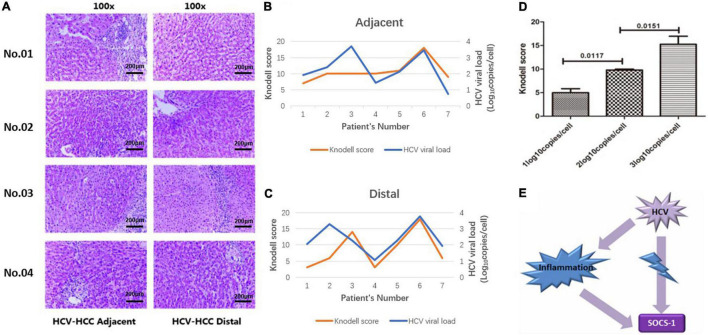
FIGURE 2.
Histological inflammation in non-HCC liver tissues with HCV infection (including adjacent and distal tissues). (A) Representative image of HE-stained non-HCC liver tissue with HCV infection (scale bar = 200 μm). (B) The correlation between HCV viral load and Knodell scores in adjacent tissues of HCV-HCC. (C) The correlation between HCV viral load and Knodell scores in distal tissues of HCV-HCC. (D) Knodell scores in non-HCC tissues with different viral loads. Knodell score in tissues with a high viral load was higher compared to tissues with a low viral load. (E) Sketch map: Histological inflammation would induce expression of SOCS-1. HCV infection-induced inflammation may interfere with the correlation between HCV and SOCS-1 expression (Mann–Whitney U test).