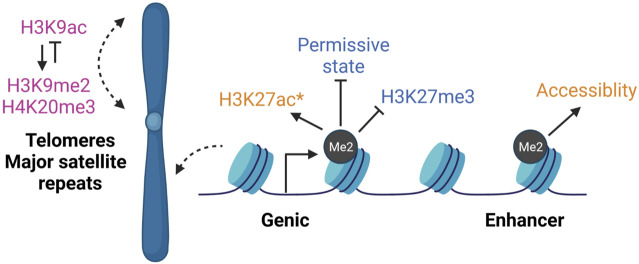
FIGURE 4.
DOT1L epigenetic cross-talk. DOT1L inhibition largely does not affect gene expression even though H3K79me is enriched on the bodies of thousands of actively transcribed genes. However, H3K79me2 participates in various epigenetic networks that may not have immediate transcription effects. In DOT1L-KO ESCs (pink), repetitive regions like telomeres and major satellite repeats lose H3K9me2 and H3K20me3, and gain H3K9ac (Jones et al., 2008). During reprogramming (blue), DOT1L inhibition promotes a permissive state that allows OCT family members bind (Kim et al., 2021). In contrast, H3K79me2 opposes spread of H3K27me3 into active genes (Onder et al., 2012). During neuronal differentiation from ESCs (orange), DOT1Li reduces enhancer accessibility and decreases H3K27ac (*at select downregulated genes) (Ferrari et al., 2020). Thus, H3K79me2 has been reported to modulate both activating and repressive modifications, indicating both cell type- and local chromatin-specific effects, rather than a single global cross-talk mechanism. Created with BioRender.com.