Figure 3.
Exosomal non-coding RNAs and the non-immune tumor microenvironment
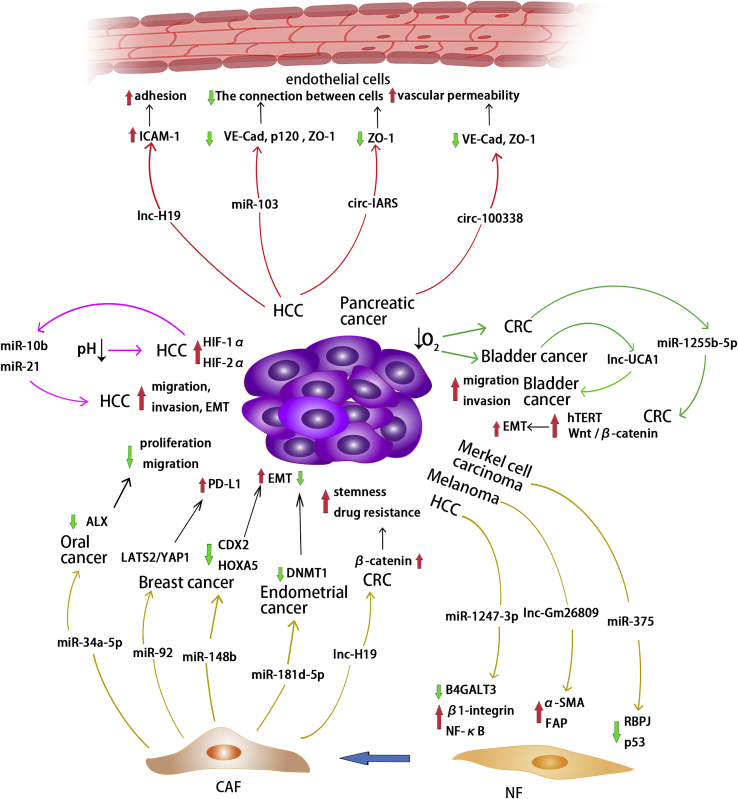
Exosomes derived from HCC, melanoma, and Merkel cell carcinoma deliver non-coding RNAs to regulatory targets and signaling pathways in fibroblasts, thereby promoting the transformation of NFs into CAFs. Exosomal non-coding RNAs derived from CAFs also regulate corresponding molecules, thereby affecting the progression of tumor cells in oral cancer, breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and CRC. Exosomes derived from HCC contain lnc-H19, which regulates ICAM-1 and promotes endothelial cell adhesion. Exosomes derived from HCC and pancreatic cancer contain non-coding RNAs that inhibit intercellular adhesion molecules and improve vascular permeability. In HCC, tumor cells in an acidic environment secrete exosomal miR-10b and miR-21 to promote tumor cell migration, invasion, and EMT. In addition, exosomal non-coding RNAs derived from CRC and bladder cancer cells in hypoxic environments promote tumor EMT, migration, and invasion.