Figure 6.
Exosomal non-coding RNAs have an effect on angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis
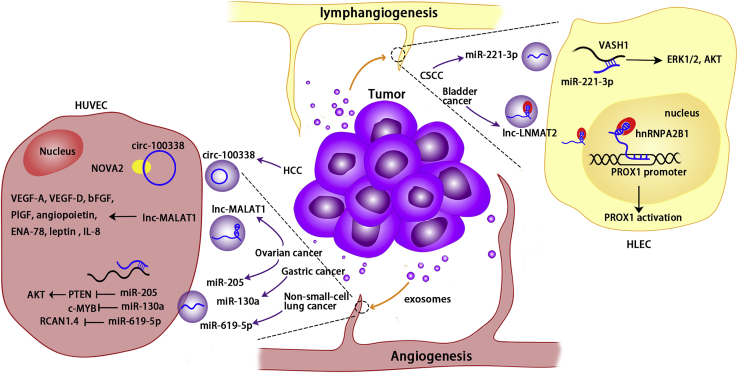
Cancer-cell-derived exosomal non-coding RNAs regulate targets and pathways in vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells, thereby promoting angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exosomal circ-100338 from HCC cells can be internalized by HUVECs and promote angiogenesis via regulating NOVA2. Cancer-derived exosomal lnc-MALAT1 and miR-205 derived from ovarian cancer cells can enter HUVECs and regulate their targets, promoting angiogenesis. Exosomal miR-130a from gastric cancer cells promotes angiogenesis via c-MYB in HUVECs. Exosomal miR-619-5p from non-small cell lung cancer cells can enter HUVECs and regulate RCAN1.4 to promote angiogenesis. Exosomal lnc-LNMAT2 derived from bladder cancer cells can enter HLECs’ nuclei and activate PROX1 via hnRNPA2B1, thereby promoting lymphangiogenesis. In CSCC, miR-221-3p from cancer cells can be internalized and inhibit VASH1, thereby promoting lymphangiogenesis via ERK1/2 and AKT.