Figure 11.
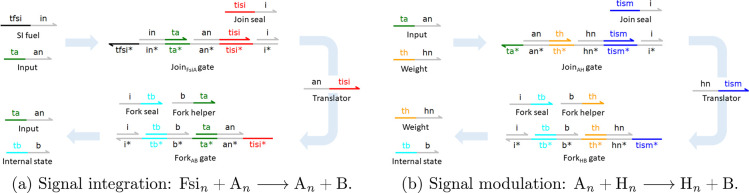
Mapping the CRN neuron to a DNA neuron. We use a two-domain Join–Fork gate to emulate each of the catalytic reactions in the CN (Table 4). In each case, a Join gate binds the two reactants in sequence, first displacing a waste molecule and second displacing a translator molecule, which triggers the corresponding Fork gate to release strands representing the reaction products. Translator displaces the first product, and then a Fork helper displaces the second product. Both Join and Fork gates can be sealed upon binding of an appropriate auxiliary strand (labeled Join seal and Fork seal), which displaces the final incumbent bound <i> strand.