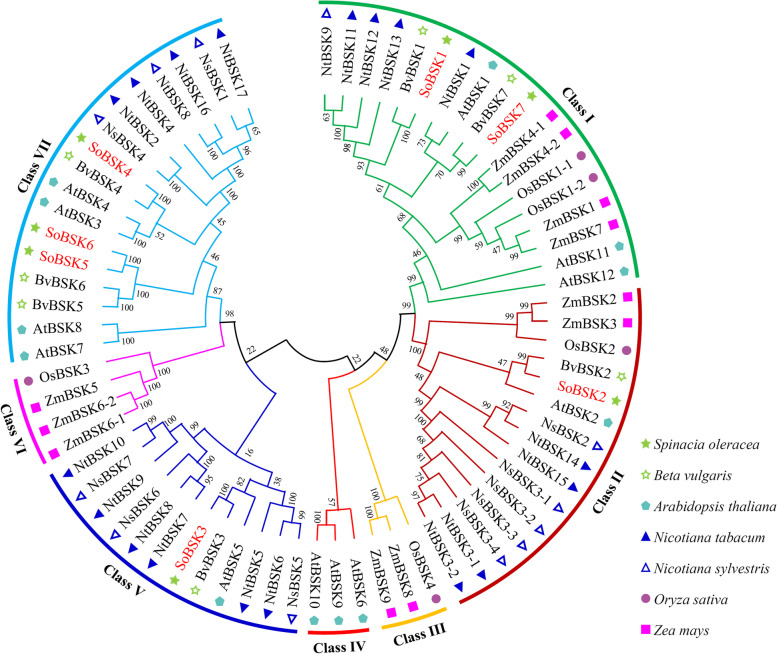
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of brassinosteroid-signaling kinases (BSKs) from spinach and other six representative plants. The phylogenetic tree was built based on the complete amino acid sequences of the BSKs by MEGA4-X with the maximum likelihood method, which indicated the phylogenetic relationships among 72 BSKs from spinach (Spinacia oleracea), sugar beet (Beta vulgaris), Arabidopsis thaliana, rice (Oryza sativa), maize (Zea mays), as well as common tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) and woodland tobacco (Nicotiana sylvestris). The colored ranges indicated the total BSK proteins classed into seven classes. Various shapes represented different plant species. The accession numbers, coding sequences (CDSs), and amino acid sequences of these BSKs were listed in Additional file 1. Bootstrap = 1000