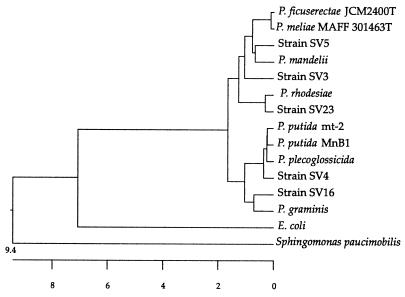
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic tree based on a comparison of 1,499 positions in the 16S rDNA sequences of Pseudomonas sp. SV strains, representative of each ARDRA subgroup, and eight neighboring sequences from the GenBank database (accession numbers are shown in parentheses): P. putida MnB1 (U70977), P. putida mt-2 (L28676), P. plecoglossicida (AB009457), P. mandelii (AF058286), P. graminis sp. nov. (Y11150), P. ficuserectae JCM2400T (AB021378), P. meliae MAFF 301463T (AB021382), and P. rhodesiae (AF064459). The 16S rDNA sequences of Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain UT26 (AF039168) and E. coli (A14565) were used as outgroups. Groups of SV strains determined by ARDRA were as follows: (i) SV1, SV2, SV4, SV20, and SV25; (ii) SV9, SV10, SV11, SV12, SV13, SV15, SV16, SV17, SV19, SV20, SV22, and SV24; (iii) SV3; (iv) SV5; and (v) SV23 (boldface strain names appear in the tree). The tree was constructed by using CLUSTAL V. The scale below the tree indicates the sequence distances as the number of substitutions per 100 nucleotides.