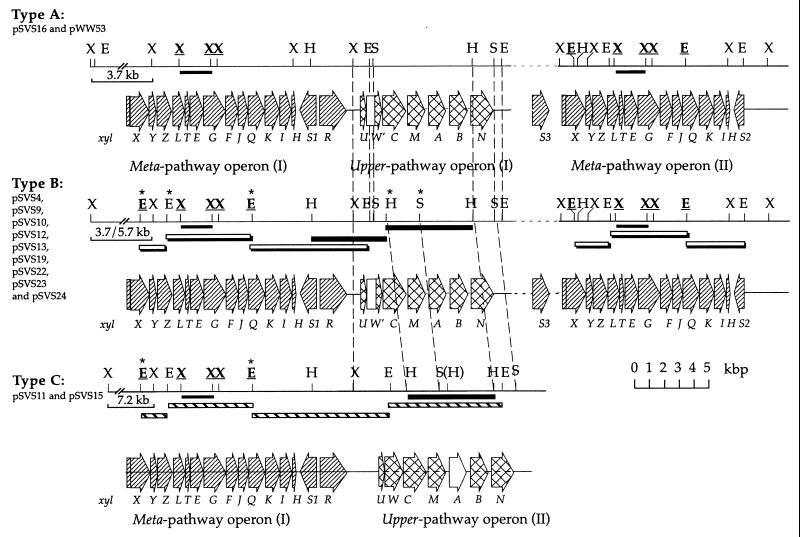
FIG. 3.
Comparative organization of xyl genes on the different pSVS plasmids and pWW53. Locations of individual genes are marked with hatched and cross-hatched arrows, the directions of which indicate the direction of transcription. The abbreviations for restriction enzyme sites are as follows: E, EcoRI; H, HpaI; S, SpeI; and X, XhoI. Only XhoI recognition sites within and close to meta pathway operons are shown. Restriction sites conserved among meta pathway operons are underlined and in boldface, those absent from pSVS16 are marked by asterisks, and the one in parentheses is present only in pSVS15. The area between upper operon I and meta operon II and xylS3 are indicated by horizontal broken lines to indicate longer distances (see Fig. 4 for exact distances). Vertical broken lines connect the identical restriction sites within and close to the upper pathway operons. Note a 1.0-kb longer spacing between upper pathway operon I and meta pathway operon I in pSVS11 and pSVS15 than between those in plasmids of types A and B. Doubly shaded bars below the restriction maps indicate the EcoRI fragments cloned from pSVS13; those from pSVS11 are shown by hatched bars. The 2.1-kb XhoI fragments which were cloned from pSVS11, pSVS15, pSVS13, and pWW53 for sequencing are indicated by thin black bars. Thick black bars indicate the HpaI fragments cloned into pCVS31, pCVS32, and pCVS42 (Table 2). A 370-nucleotide region upstream of xylC in plasmids of types A and B is 99% identical to the ntnW gene of P. putida TW3 (93 and 96% identical to xylW in pWW0 and pDK1, respectively) but is preceded by a region without any homology to xylW (open box). The open arrow for the xylA sequence of pSVS11 and pSVS15 depicts its distinct low homology to the other xylA sequences, as opposed to the surrounding xylC, xylM, xylB, and xylN sequences.