Fig. 7.
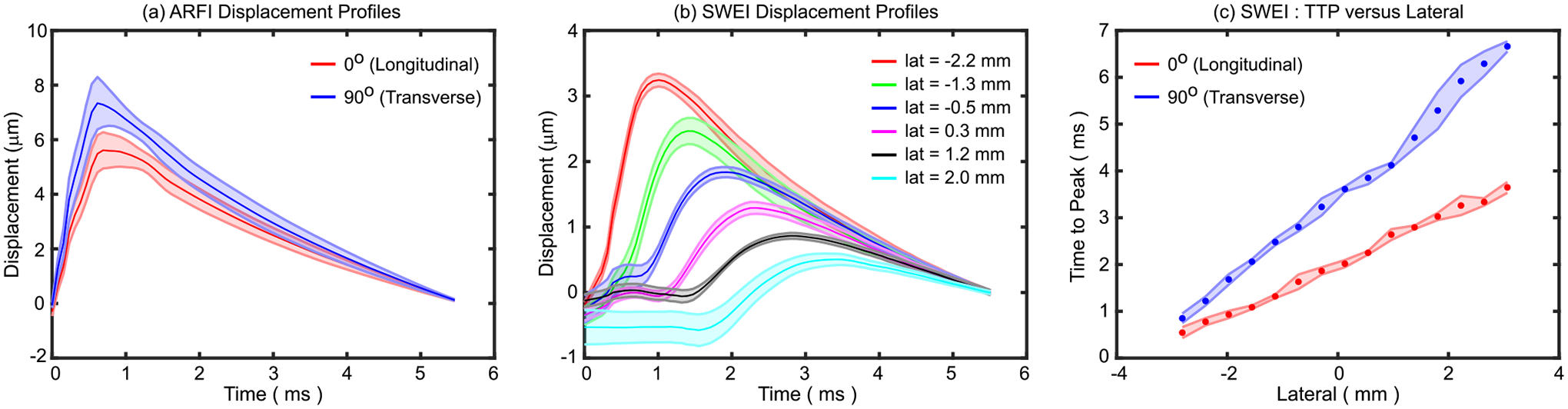
(a) ARFI displacement profiles in excised pig biceps femoris muscle when the lateral aspect of the transducer is oriented at 0° (red) and 90° with respect to muscle fibers. Data are plotted as median (solid line) ± 0.5×interquartile range (IQR, shaded region) over the 2D region of interest (ROI) shown in Fig. 8. (b) SWEI displacement profiles when the transducer is oriented at 0° with respect to muscle fibers. Data are plotted as median (solid line) ± 0.5×IQR (shaded region) in the same muscle over the axial range shown for the ROIs in Fig. 8 at 6 different lateral locations. The lateral location of the ARF excitation was −3.4 mm. (c) Time to peak (TTP) versus lateral distance when the transducer was oriented at 0° (red) and 90° (blue) with respect to muscle fibers for the calculation of the shear wave velocity. Data are plotted as median (circle marker) ± 0.5×IQR (shaded region) over the axial range shown for the ROI in Fig.8.
