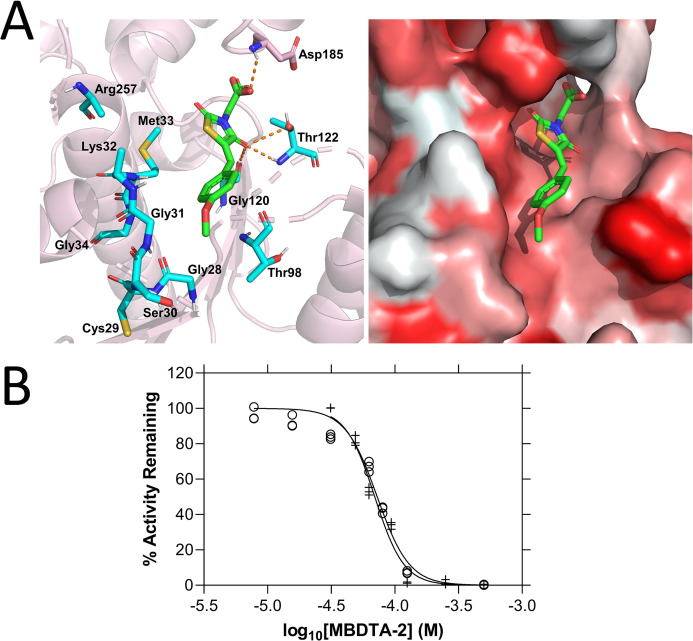
Figure 4. Mode of AtDHDPR2 inhibition by (Z)-2-(5-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid (MBDTA-2).
(A) The predicted MBDTA-2 (green)-binding site resulting from static docking with AtDHDPR2 (PDB ID: 5UA0) overlaps with the probable NADPH cofactor-binding site (cyan, left panel). Hydrophobicity of the predicted binding pocket (right panel) is represented by white-red shading indicating hydrophilic–hydrophobic residues. (B) Dose–response curves of MBDTA-2 against AtDHDPR1 (⚬) and AtDHDPR2 (+) enzymes in the presence of saturating concentrations of substrate and cofactor. Data were fitted to a nonlinear regression model (solid line), resulting in R2 values of 0.97 and 0.98 for AtDHDPR1 and AtDHDPR2, respectively.