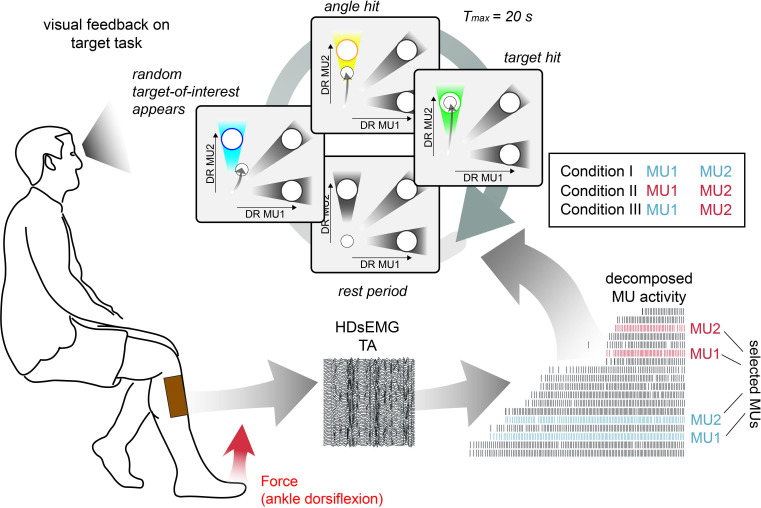
Figure 2. Schematic overview of the target task.
High-density surface electromyogram (HDsEMG) of tibialis anterior muscle (TA) was acquired and decomposed from the underlying neural activity in real time. Concurrently, the force due to dorsiflexion of the ankle (red arrow) and bipolar electromyogram (EMG) of fibularis longus (FL), lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle (GL), and medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle (GM) were recorded. The identified motor unit (MU) pool was ranked accordingly to the recruitment order. Two pairs of MUs with a similar recruitment threshold were selected from the initial (blue) and the latter recruited half (red). During the target task, subjects were instructed to navigate a cursor inside a 2D space by modulating the normalised discharge rate (DR) of MU1 and MU2. The selection of MU1 and MU2 was determined by three different conditions. In condition I, MU1 and MU2 were coming from the low recruitment threshold pair (blue), in condition II from the high recruitment threshold pair (red), while in condition III, the lowest threshold MU of the low threshold pair was pooled with the highest threshold MU of the high threshold pair. During the target task, subjects were asked to stay inside the origin until the target-of-interest (blue) appeared (randomly selected). By navigating the cursor inside the angle area around the target-of-interest, subjects were granted an angle hit (yellow). The trial was terminated when either the subject managed to place and hold the cursor inside the target area (target hit, green) or more than 20 s had passed since the target-of-interest appeared. In each condition, 30 targets are shown, that is, each target 10 times.