Fig. 6.
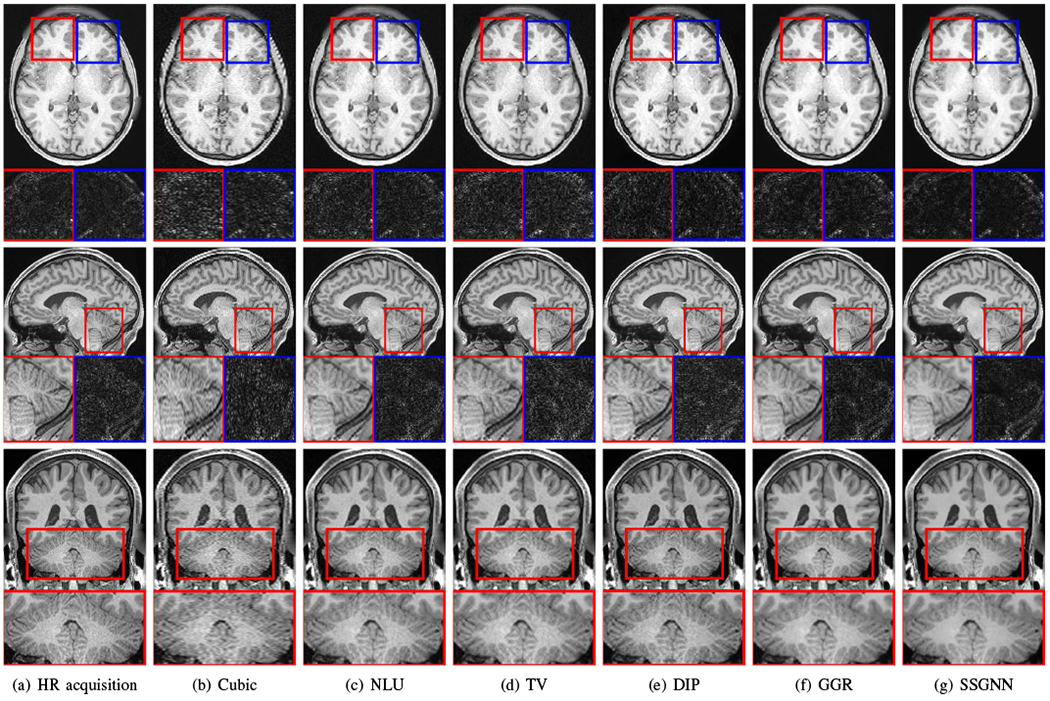
Slices from the direct HR acquisitions and HR reconstructions on the HCP dataset. The top line shows the comparisons in the axial slices and noise levels. The noise detected from the highlighted patches is shown below the axial slices. The results show that our approach (SSGNN) performed the best in noise suppression, and considerably reduced the noise compared to the HR acquisition. The middle line shows the comparisons in the sagittal slices and their noise levels. SSGNN offered the best qualitative results according to the image details and noise suppression, particularly in the cerebellum as highlighted in the images. The bottom line shows the results in the coronal plane. SSGNN yielded the best image quality. In particular, SSGNN offered finer anatomical structures of the cerebellum at a lower noise level, and in turn, achieved superior reconstructions to the direct HR acquisitions as well as the five baselines.
