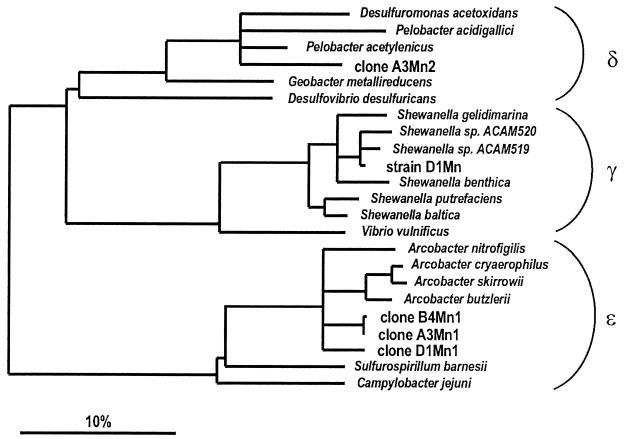
FIG. 5.
16S rRNA-based tree reflecting the phylogenetic relationships of the clone sequences and a selection of sequences belonging to different subclasses of Proteobacteria. The tree is based on the results of a maximum parsimony analysis including complete or almost complete 16S rRNA sequences from representative bacteria of a phylogenetic branch. The topology of the tree was evaluated and corrected according to the results of distance matrix, maximum parsimony, and maximum likelihood analyses of various data sets. Branching patterns within each subclass were also evaluated by using a 50% conservation filter for the members of their corresponding subclass (41). Multifurcations indicate topologies that could not be unambiguously resolved. The bar indicates 10% estimated sequence divergence. EMBL accession numbers of the new sequences are as follows: A3Mn2, AJ271656; D1Mn, AJ271657; B4Mn1, AJ271653; A3Mn1, AJ271655; and D1Mn1, AJ271654.