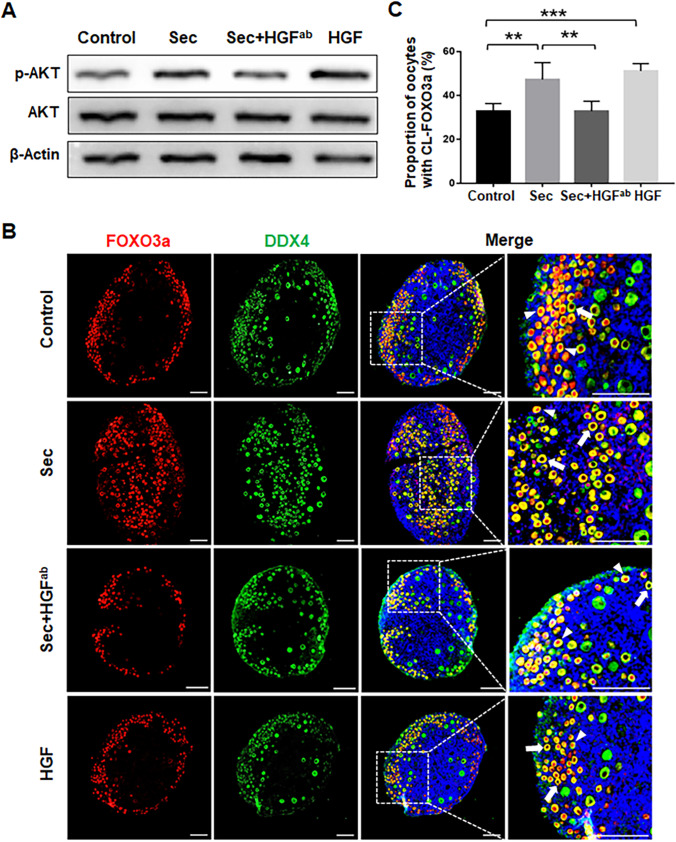
Fig. 3.
HGF secreted from hUC-MSCs promoted the activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway. A. Western blot showing the expression of p-AKT in mouse ovaries after 4 days of in vitro culture. The ability of the hUC-MSC-sec to increase the phosphorylation of AKT was greatly inhibited by the addition of HGFab. The expression of p-AKT was significantly increased in the HGF-treated group compared to controls. B. Immunofluorescence analysis showing the location of FOXO3a in mouse ovaries after 4 days of culture. The ability of the hUC-MSC-sec to promote FOXO3a cytoplasmic translocation was inhibited by the addition of HGFab. The arrowheads indicate the nuclear localization of FOXO3a, and the arrows indicate the cytoplasmic localization of FOXO3a. C. The proportion of CL-FOXO3a was significantly decreased in hUC-MSC-sec plus HGFab-treated ovaries (32.8 ± 4.6%) compared to the hUC-MSC-sec group (47.3 ± 7.7%). The proportion of CL-FOXO3a was significantly increased in HGF-treated ovaries (50.9 ± 3.1%), which was similar to the hUC-MSC-sec group, compared to controls (32.8 ± 3.5%). Data are shown as the mean ± SD, n = 6. **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Scale bars, 100 μm