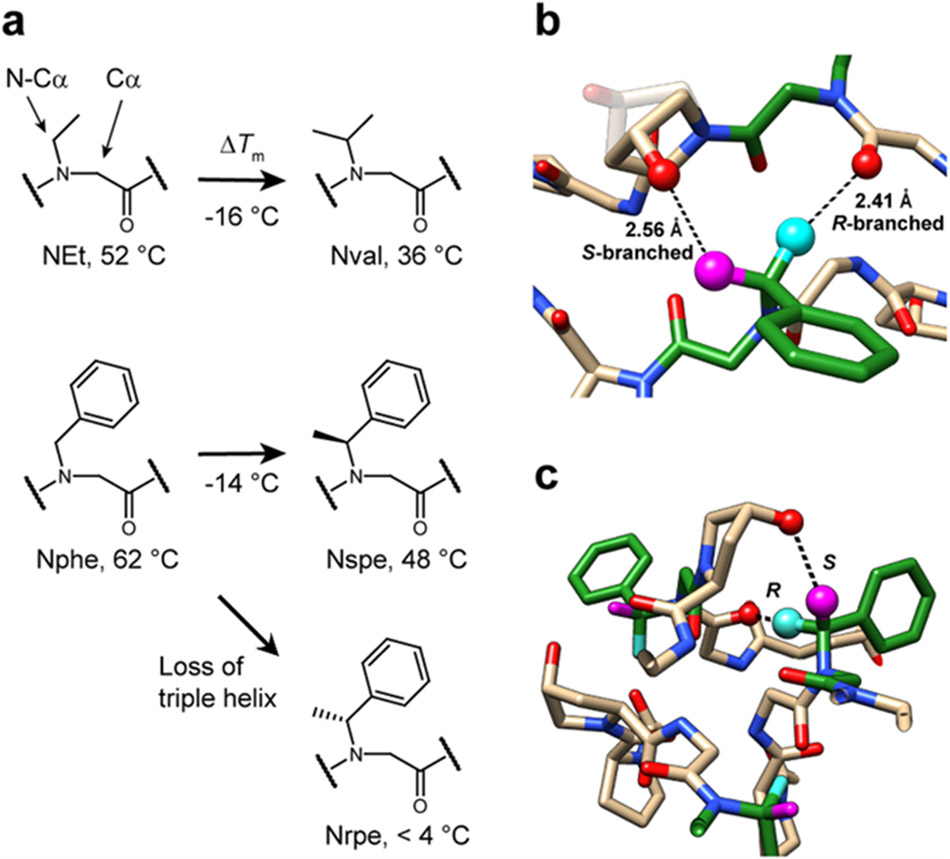
Figure 5. N-Cα branching of peptoid residues affects triple-helical folding.
a, Nval- and Nspe-CMPs, each containing an N-Cα branch, had Tm values 14-16 °C lower than their unbranched analogs: NEt and Nphe. Moreover, while Nspe conferred a triple-helix with a Tm of 48 °C, its enantiomer, Nrpe completely abolished the triple-helical folding. b,c, Molecular modeling based on the crystal structure of Nphe-CMP showing potential steric clashes within the triple-helix introduced by the N-Cα methyl branch. The R-branch of Nrpe (cyan), pointing directly toward the inner core of the triple-helix, may clash with the backbone carbonyl of the cross-chain Gly and interfere with proper backbone assembly. In contrast, the S-branch (magenta) in Nspe may clash with the hydroxyl group of a cross-chain Hyp, which may be less destabilizing since the steric repulsion may be alleviated by changing the Hyp’s ring pucker (shown with half-transparency in b).