FIGURE 3.
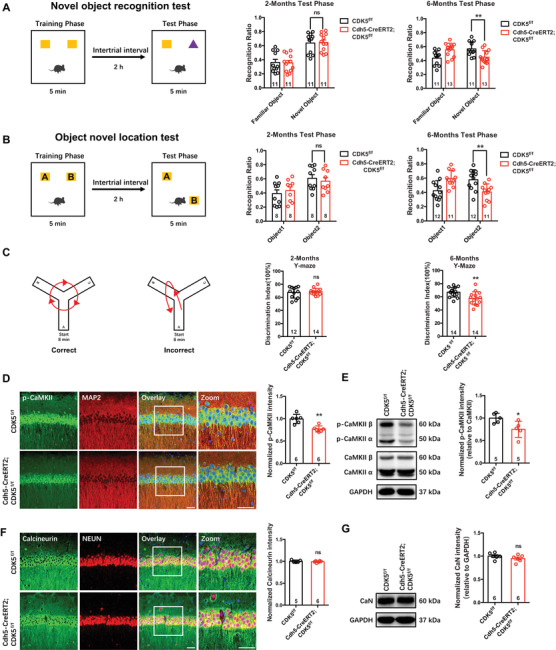
Persistent seizures lead to hippocampus‐dependent memory impairment. (A–C) Hippocampus‐dependent memory behaviors were performed in CDK5f/f and Cdh5‐CreERT2;CDK5f/f mice. The schematic diagram of novel object recognition test and the discrimination index value (A), the schematic diagram of object new location memory and the discrimination index value (B), the schematic diagram of Y‐maze and the discrimination index value (C). (D and E) Representative phospho‐CaMKII (p‐CaMKII, Thr286) (green) staining in CA1 of mice (D, left, counterstained with microtubule‐associated protein 2 [MAP2] [red] and nuclear marker DAPI [blue]) and quantification of normalized p‐CaMKII intensity (D, right, **p < 0.01, Student's t‐test). Representative immunoblotting bands of p‐CaMKII (Thr286), CaMKII, and GAPDH (E, left), and quantitative analyses by densitometry for p‐CaMKII, *p < 0.05 (E, right). (F and G) Representative calcineurin (CaN) (green) staining in CA1 of mice (F, left, counterstained with neuronal marker [NEUN] [red] and nuclear marker DAPI [blue]) and quantification of normalized CaN intensity (F, right, ns: not significant, Student's t‐test). Representative immunoblotting bands of CaN and GAPDH (G, left), and quantitative analyses by densitometry for CaN (G, right). Scale bar: 20 μm, magnified images: 50 μm
