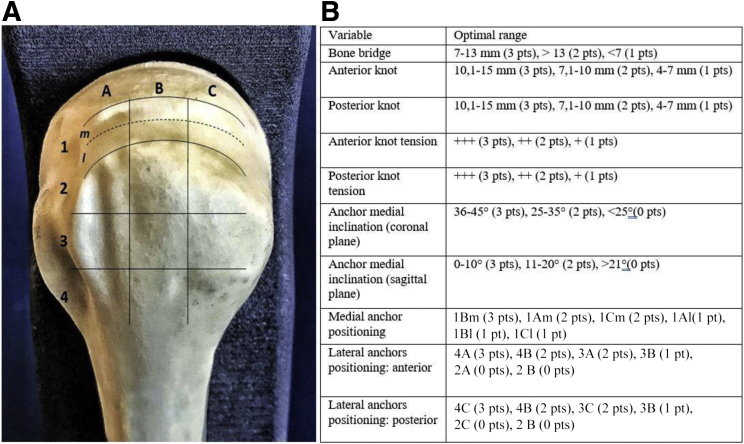
Fig 1.
(A) Proximal humerus. Left side. Posterior view. To precisely localize anchor position, the greater tuberosity was divided into 3 equal zones in the sagittal plane (A-C), and four rows (1-4) were defined in the coronal plane. Row 1 consists of the area included from the articular surface to the summit of the greater tuberosity and is subdivided in medial (m) strictly adjacent to the cartilage (A1m, B1m, C1m), and lateral (l) (A1l, B1l, C1l); Row 2 (A2, B2, C2), 0 to 7 mm below the summit; Row 3 (A3, B3, C3), 8 to 14 mm below row; Row 4 (A4, B4,C4), 15 to 21 mm below row. (B) Anchor positioning was scored. Quality variables: For each of the qualitative variables, points were assigned on the basis of a specifically predetermined numerical reference system: for the Bone Bridge from 7 to 13 mm three points were assigned, for more than 13 mm were assigned two points, one point was awarded for less than 7 mm. For the anterior tendon bridge, three points between 10.1 and 15 mm were assigned, between 7.1 and 10 mm, two points were assigned and one point was assigned between 4 and 7 mm. For the posterior tendon bridge, three points between 10 and 15 mm were assigned, two points between 7.1 and 10 mm and one point between 4 and 7 mm. To evaluate the tension of the anterior and posterior knots, 3 points were assigned when the tightness of the knots was optimal, when the tightness was intermediate, two points were assigned, and one point was assigned when the tightness was poor. The evaluation of the inclination of the medial anchor on the coronal plane was made by attributing three points from 36° to 45°, two points between 25° and 35°, and zero points for values less than 25°. The inclination of the medial anchor on the sagittal plane was evaluated by attributing three points from 0° to 10°, attributing two points between 11° and 20° and zero points for values greater than 21°. The positioning of the anchors was evaluated on the basis of the scheme (Table 3A). For the positioning of the medial anchor three points in 1Bm, two points in 1 Am and 1Cm, one point in 1Al, 1Bl, and 1Cl were attributed. For the positioning of the front lateral anchor, three points were attributed in 4C, two points in 4B, 3C, one point in 3B, zero points in 2B, 2C. For the positioning of the rear lateral anchor three points in 4C, two points in 4B and 3C, one point in 3B, zero points in 2C and 2B were attributed.