Figure 2 |. Genetic correlation among SUD traits and other phenotypes.
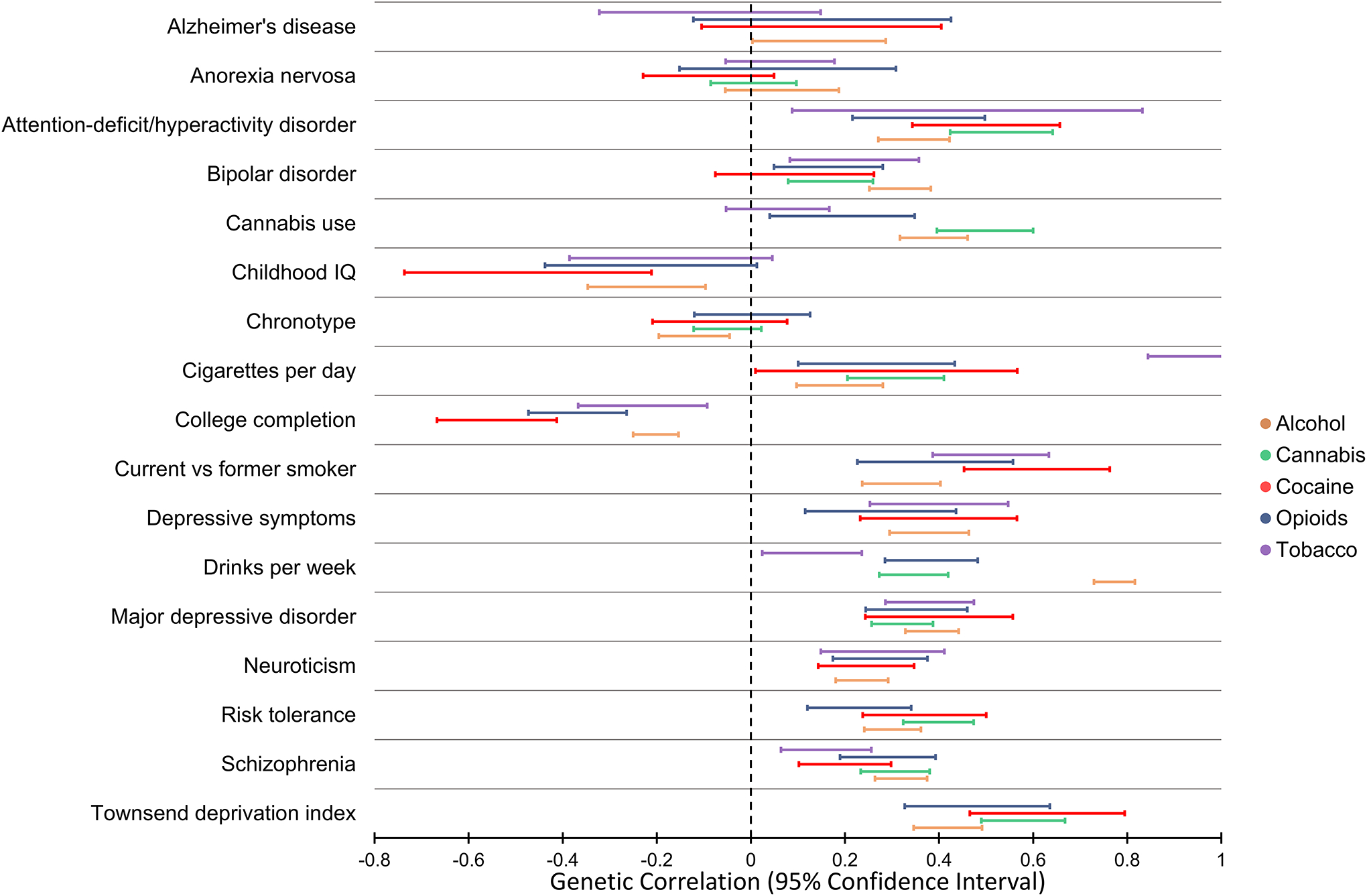
Genetic correlation of problematic alcohol use, cannabis use disorder, cocaine dependence, opioid use disorder, and nicotine dependence with psychiatric disorders, behavioural traits, and other complex phenotypes. The 95% confidence interval of the genetic correlation estimates were obtained from previous studies13, 37, 44, 48, 185 that applied the linkage disequilibrium score regression method. The traits included are those tested with respect to at least four out of the five addictions considered. There are some patterns of genetic correlation that are consistent across the five addictions presented. The major differences among them are related to the substance-specific genetic correlations, i.e. nicotine addiction vs. cigaretters per day, alcohol addiction vs. drinks per week, and cannabis addiction vs. cannabis use.
