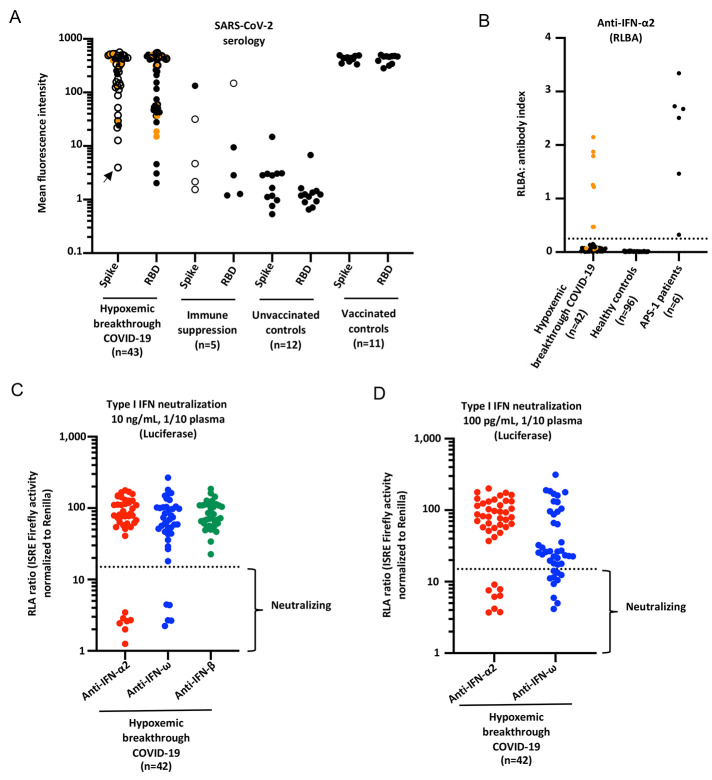
Fig. 1.
Neutralizing auto-antibodies (Abs) against IFN-α2 and IFN-ω in patients with hypoxemic breakthrough COVID-19 despite a normal serological response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. (A) SARS-CoV-2 serology against spike(S)-protein and receptor binding domain (RBD) in hypoxemic breakthrough COVID-19 (N=43), patients with immune suppression (n=5), unvaccinated controls (N=12), and vaccinated and uninfected healthy controls (n=11). Mean fluorescence intensity is shown. The orange dots correspond to the 10 individuals with auto-Abs neutralizing type I IFNs. Empty circles represent either Spike or RBD serology, to outline the highest value for one patient. The arrow represents the patient without B cell deficiency but with an insufficient Ab response to the virus. (B) Radioligand binding assay (RLBA) results for auto-Abs against IFN-α2 in patients with hypoxemic breakthrough COVID-19 pneumonia without immune suppression or low Ab response to the vaccine (N=42), uninfected controls (N=96), and uninfected APS-1 patients (N=6). (C) Neutralization of 10 ng/mL IFN-α2, IFN-ω or IFN-β in the presence of plasma 1/10 from patients with hypoxemic breakthrough COVID-19 pneumonia with a good Ab response to the vaccine (N=42). Relative luciferase activity is shown (ISRE dual luciferase activity, with normalization against Renilla luciferase activity) after stimulation with 10 ng/mL IFN-α2 or IFN-ω in the presence of plasma 1/10. RLA: relative luciferase activity. (D) Neutralization of 100 pg/mL IFN-α2 or IFN-ω in the presence of plasma 1/10 from patients with hypoxemic breakthrough COVID-19 pneumonia with a good Ab response to the vaccine (N=42).