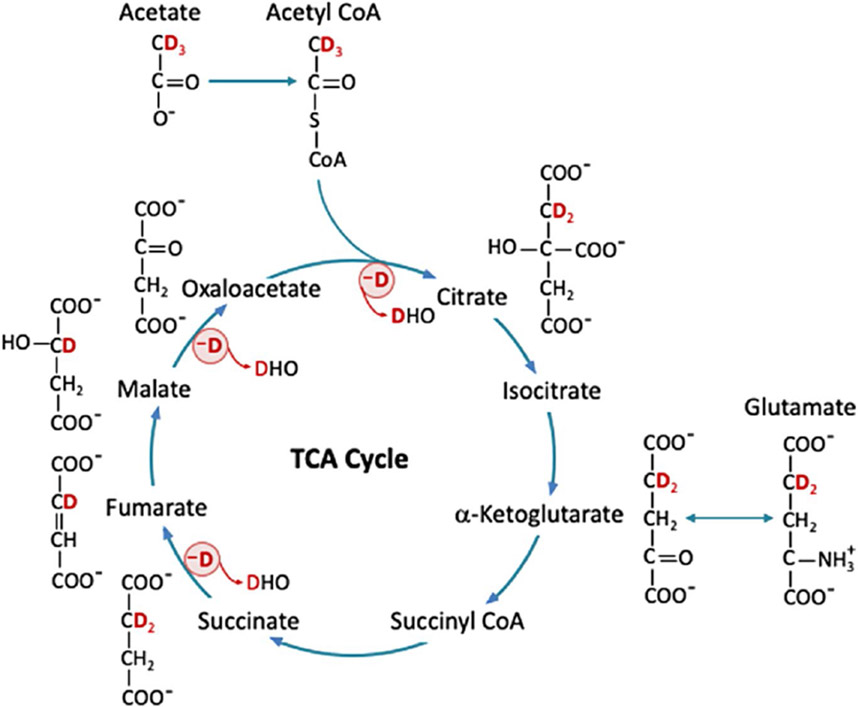
FIGURE 2.
Acetate labeled with three 2H atoms ([2,2,2-d3]-acetate) is converted to acetyl-CoA, which then enters the TCA cycle and is converted to citrate and α-ketoglutarate, with possible loss of one 2H atom. Meanwhile, α-ketoglutarate can exchange with glutamate to produce [4,4-d2]-glutamate. Then, succinyl-CoA is generated and followed by the conversion from succinate to fumarate with possible loss of another 2H atom. Finally, fumarate is converted to malate, which then turns into oxaloacetate with possible loss of the last 2H atom. The deuterium lost via the TCA cycle could end up in HDO. Deuterium-labeled acetate or other substrates, glutamate, and HDO can be measured by DMRSI; other intermediates are below detectable concentration. DMRSI, deuterium (2H) MRS imaging; HDO, deuterated water; TCA, tricarboxylic acid