Fig. 1. Pathways for the debulking of TOP-DPC.
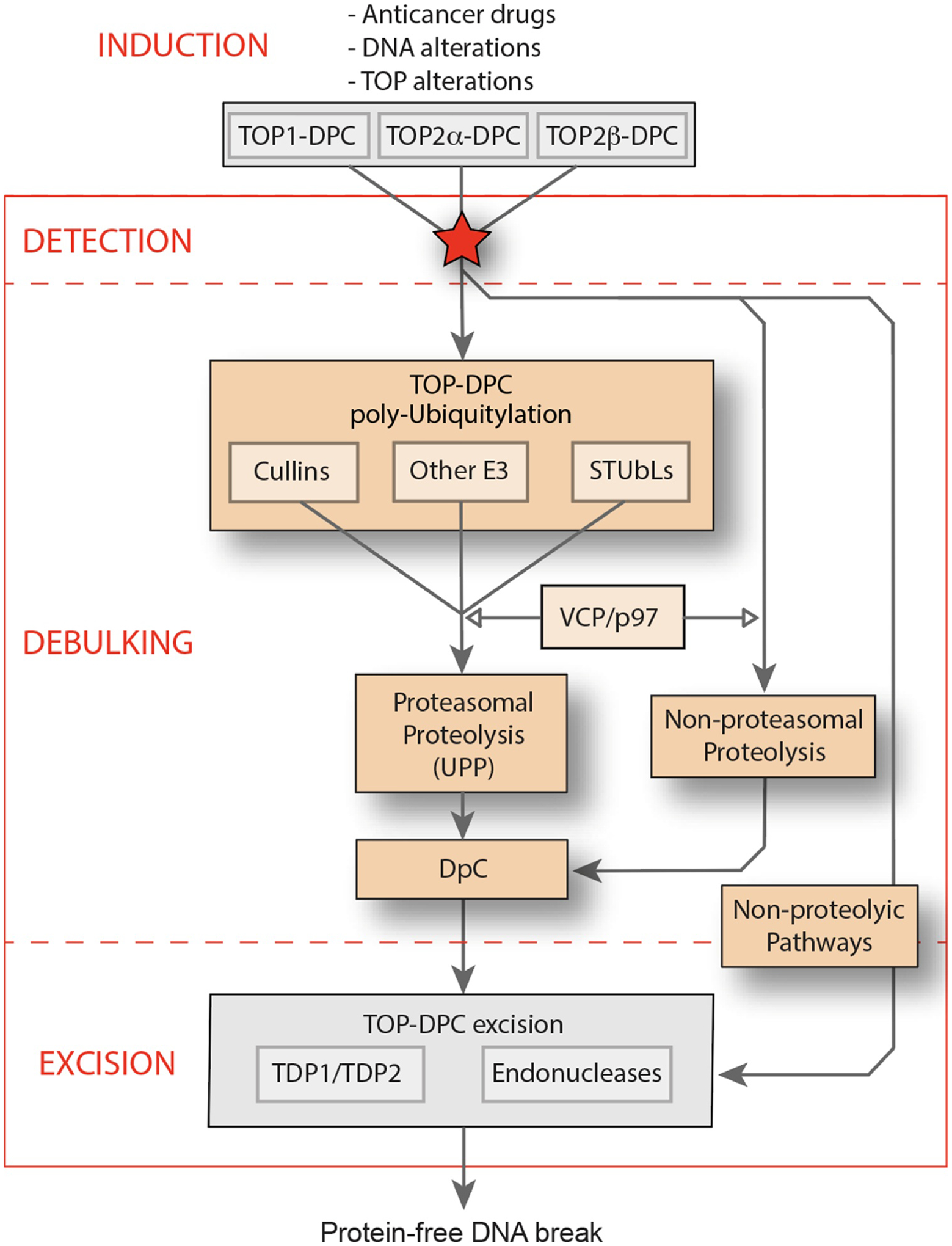
Overall scheme for the induction and excision repair of TOP-DPC. The ubiquitin proteasomal pathway (UPP) is represented in the middle with the different ubiquitin pathways for TOP-DPC (Cullins, SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases [STUbLs]). The non-proteasomal pathway is examplifed by Spartan/Wss1. Both the proteasomal and non proteasomal generate DNA peptide crosslinks (DpC). The non-proteolytic pathways shown as the arrow at right includes the endonuclease pathway (examplified by MRE11) and the ZATTZNF451 pathway, which unfolds TOP2-DPC and primes their hydrolytic removal by TDP2 [125]. TOP-DPC excision is detailed in a separate issue of DNA Repair [1].
