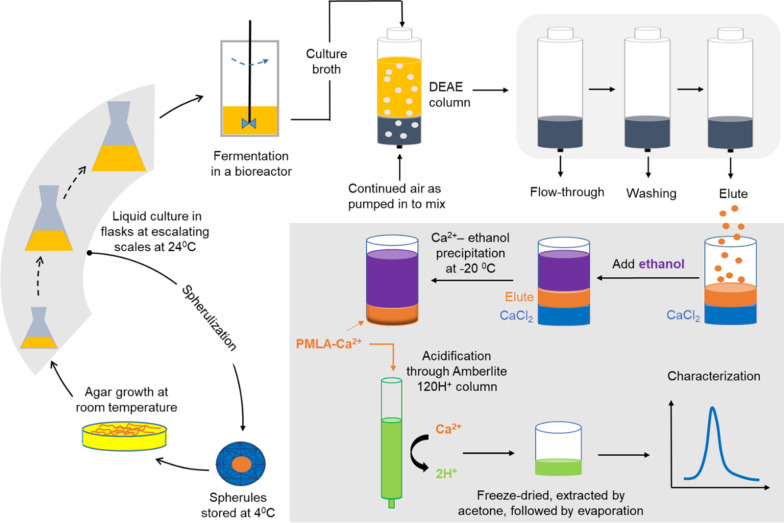
Fig. 4.
Schematic presentation of PMLA bioproduction by plasmodia of P. polycephalum. Spherules, originally kept at 4 °C, are activated to grow on agar before the microplasmodia are removed for liquid culture in 100-, 500-, and 2000-mL-volume flasks with gradually increasing volumes, ending in a typical 10-L fermentation in a bioreactor. During these amplification liquid-culture steps, spherules can be prepared for storage. The resulting culture broth from fermentation is passed through DEAE-cellulose columns, followed by washing and elution [59]. PMLA-Ca2+ is then acquired by mixing the elutes with a CaCl2 solution, precipitated by adding ice-cold ethanol, further collected, lyophilized to be redissolved in water, and finalized by acidification using an Amberlite ion exchange resin to yield PMLA-H+. This final PMLA-H+ product needs to be well characterized before its use in biological applications