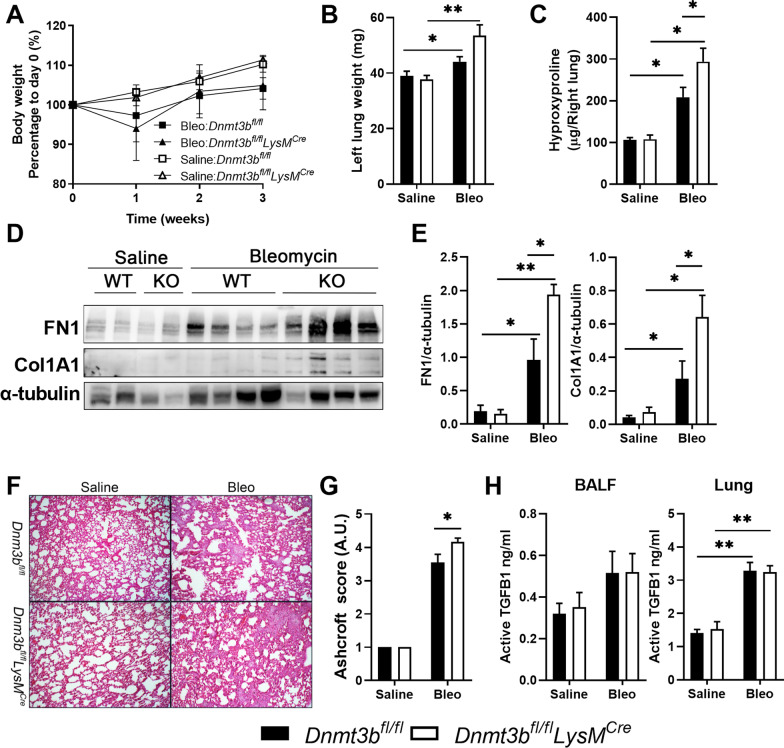
Fig. 3.
Myeloid DNMT3B deficiency promotes bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis. A Body weight of control (Dnmt3bfl/fl) and DNMT3B conditional knockout (Dnmt3bfl/flLysMcre) mice over time after bleomycin or saline treatment. B Lung weight of left lung lobes of control (Dnmt3bfl/fl) and DNMT3B conditional knockout (Dnmt3bfl/flLysMcre) mice 21 days after bleomycin (Bleo) or saline treatment. C Collagen expression as measured by hydroxyproline levels in the right lung of control (Dnmt3bfl/fl) and DNMT3B conditional knockout (Dnmt3bfl/flLysMcre) mice 21 days after bleomycin (Bleo) or saline treatment. D Representative pictures of western blot assays for the detection of Fibronectin (FN1) and Collagen type I (COL1A1) protein levels in lung homogenates of control (ctrl) and DNMT3B conditional knockout (KO) mice 21 days after bleomycin treatment. α-Tubulin serves as a loading control. E Quantification of FN1 and COL1A1 expression relative to α-tubulin levels of Western blots depicted in D. F Representative H&E-stained lung tissue sections of control (Dnmt3bfl/fl) and DNMT3B conditional knockout mice (Dnmt3bfl/flLysMcre) 21 days after saline or bleomycin treatment (20x). G Quantification of pulmonary fibrosis using the Ashcroft score in control (Dnmt3bfl/fl) and DNMT3B conditional knockout (Dnmt3bfl/flLysMcre) mice 21 days after saline or bleomycin treatment. H Active TGFB1 protein levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung homogenates of control (Dnmt3bfl/fl) and DNMT3B conditional knockout (Dnmt3bfl/flLysMcre) mice 21 days after saline or bleomycin treatment determined by ELISA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 10 mice per group (bleomycin treated) or 4 mice per group (saline control). Bleo: bleomycin; Black bars: littermate control mice, open bars: myeloid specific DNMT3B deficient mice. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01