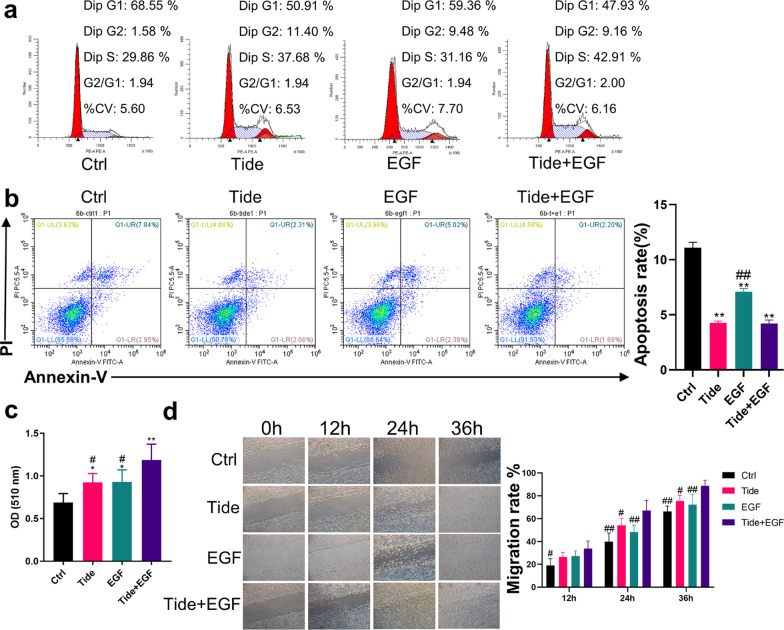
Fig. 6.
The combined use of Tideglusib and EGF could accelerate proliferation and migration of EpiSCs. EpiSCs were randomly divided into four groups that incubated with PBS, 200 nM Tideglusib, 20 ng/mL EGF, or combined use of Tideglusib and EGF dissolved in Epilife medium for 24 h. a and b Flow cytometry was used to quantify cell cycle distribution and apoptosis in cells treated with different drugs for 24 h. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. the control group. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus the combination therapy group. N = 3. c SRB assay was performed to detect the proliferation effect of drugs on EpiSCs. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus the control group. # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01 versus the combination therapy group. N = 6. d Confluent monolayers of EpiSCs were randomly divided into four groups that received PBS, 200 nM Tideglusib, 20 ng/mL EGF, or combined use of Tideglusib and EGF dissolved in Epilife medium and subjected to in vitro scratch-wound assays. N = 3. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus the combination therapy group at time-point