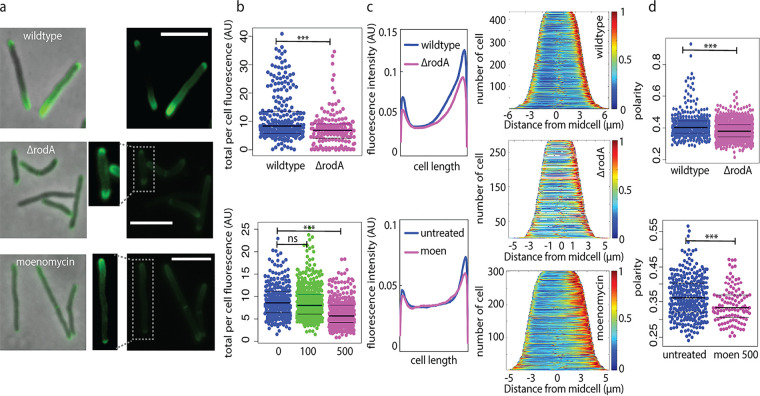
FIG 2.
RodA and aPBPs promote polar peptidoglycan synthesis under basal conditions. (a) Wild-type M. smegmatis, ΔrodA M. smegmatis, and M. smegmatis cells treated with 500 μg/mL moenomycin for 30 min were incubated with alkyne-d-alanine-d-alanine for 10 min (~5 to 6% generation time). Probe was detected by click chemistry ligation to picolyl azide AF488. All images were acquired at 1 s of exposure. Dim signal from boxed cells was enhanced for visibility. Scale bars, 5 μm. (b) Total fluorescence per cell. Moenomycin was added at 100 or 500 μg/mL. Significance was determined using t test (top) or analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by a Tukey post hoc test to conduct pairwise comparisons (bottom). ***, P < 0.001. AU, arbitrary units. (c) Fluorescence signal localization represented by mean raw fluorescence intensity profile from nonseptating cells detected using Oufti and analyzed using MATLAB (each cell was divided into 100 fragments, with each assigned an intensity value to normalize for cell length) (left) and demographs (right). (d) Polarity ratios. Moen 500, 500 μg/mL moenomycin treatment. t test, P < 0.001 for 168 < n < 433 (number of cells analyzed).