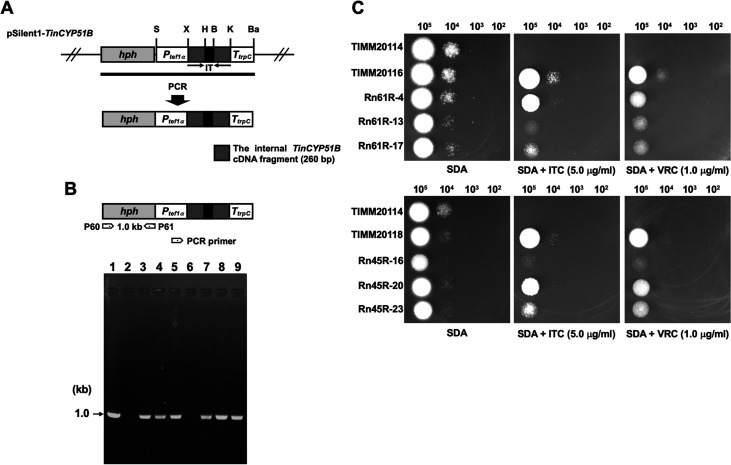
FIG 5.
RNAi-mediated downregulation of TinCYP51B in the low azole-susceptibility T. indotineae strains TIMM20116 and TIMM20118. (A) Schematic representation of the construct expressing TinCYP51B hairpin RNA in the gene-silencing vector pSilent1-TinCYP51B. Arrows indicate the direction of the TinCYP51B cDNA. The hph cassette is composed of PtrpC, hph, and Aspergillus nidulans trpC terminator (TtrpC). Plasmid DNA of pSilent1-TinCYP51B was used as a template for PCR, to amplify the sequence indicated by the thick line. Ptef1α, the promoter sequence of T. indotineae translation elongation factor 1-α (TinTef1α) gene. IT, the M. oryzae cut1 gene intron spacer. Restriction enzyme site: Ba, BamHI; B, BglII; K, KpnI; S, SpeI; X, XhoI. (B) PCR analysis of the short hairpin RNA (shRNA) clones. Genomic DNA samples from each strain were subjected to PCR with a pair of the primers P62 and P63 for amplification of the E. coli hph gene. Lanes 1 to 9, pSilent1-TinCYP51B, TIMM20116 (parent strain), the shRNA clone Rn61R-4, Rn61R-13, Rn61R-17, TIMM20118 (parent strain), Rn45R-16, Rn45R-20, and Rn45R-23, respectively. A DNA standard fragment size is shown on the left. (C) Evaluation of ITC and VRC susceptibility in the shRNA clones against the TinCYP51B gene by serial dilution drug susceptibility assays. Spores from each strain were spotted at different dilutions on SDA plates, as described in Materials and Methods. The plates were incubated at 28°C for 3 to 5 days.