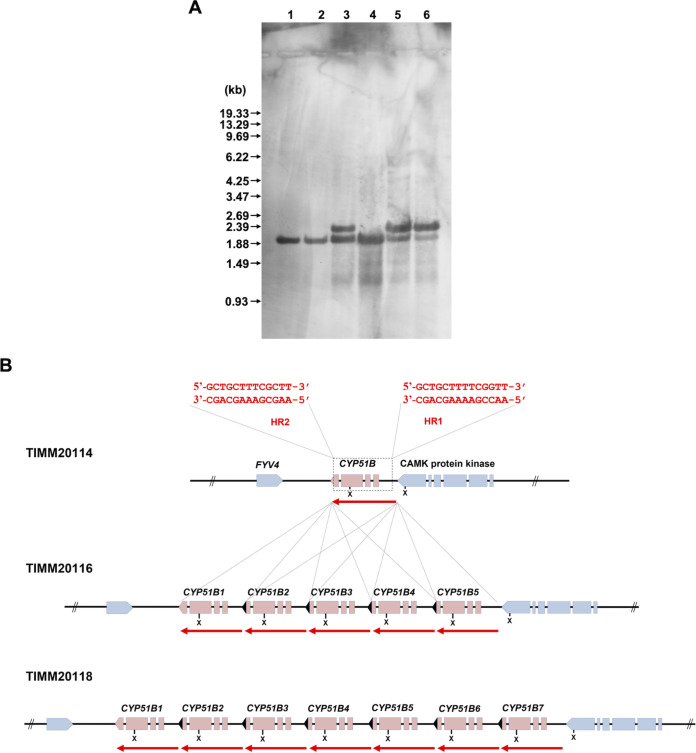
FIG 7.
Organization of the CYP51B loci within the genomes of six T. indotineae strains (TIM20114, TIMM20115, TIMM20116, TIMM20117, TIMM20118, and TIMM20119). (A) Southern blotting. Aliquots of approximately 10 μg of total genomic DNA from each strain were digested with XhoI and separated by electrophoresis on 0.8% (wt/vol) agarose gels. Lanes 1 to 6, TIMM20114, TIMM20115, TIMM20116, TIMM20117, TIMM20118, and TIMM20119, respectively. An internal fragment (about 260 bp) of the TinCYP51B cDNA was amplified by PCR with a pair of the primers P58 and P59 (Table S1) and used as a hybridization probe. DNA standard fragment sizes are shown on the left. (B) Schematic representation of the organization of the TinCYP51B genes in the six strains. The TinCYP51B genes are indicated in red, with a red arrow showing the extent of the duplicated blocks. The truncated C terminus of the recombinant copies (TinCYP51B2 to TinCYP51B5 in TIMM20116 and TIMM20119, and TinCYP51B2 to TinCYP51B7 in TIMM20118) is marked in black. The genes marked in blue are the neighboring genes. The susceptible strain TIMM20114 and the resistant strain TIMM2117 both harbor one copy of the TinCYP51B gene, whereas both TIMM20116 and TIMM20119 have the same TinCYP51B loci architecture with 5 copies. The conserved homologous recombination sites HR1 and HR2 are described in red at the top of the figure. The XhoI restriction sites at the TinCYP51B loci are also indicated (X). The sequences of the TIMM20114 and TIMM20118 CYP51B loci can be found in the supplemental material.