Figure 1. Classification and composition of magnetic soft materials.
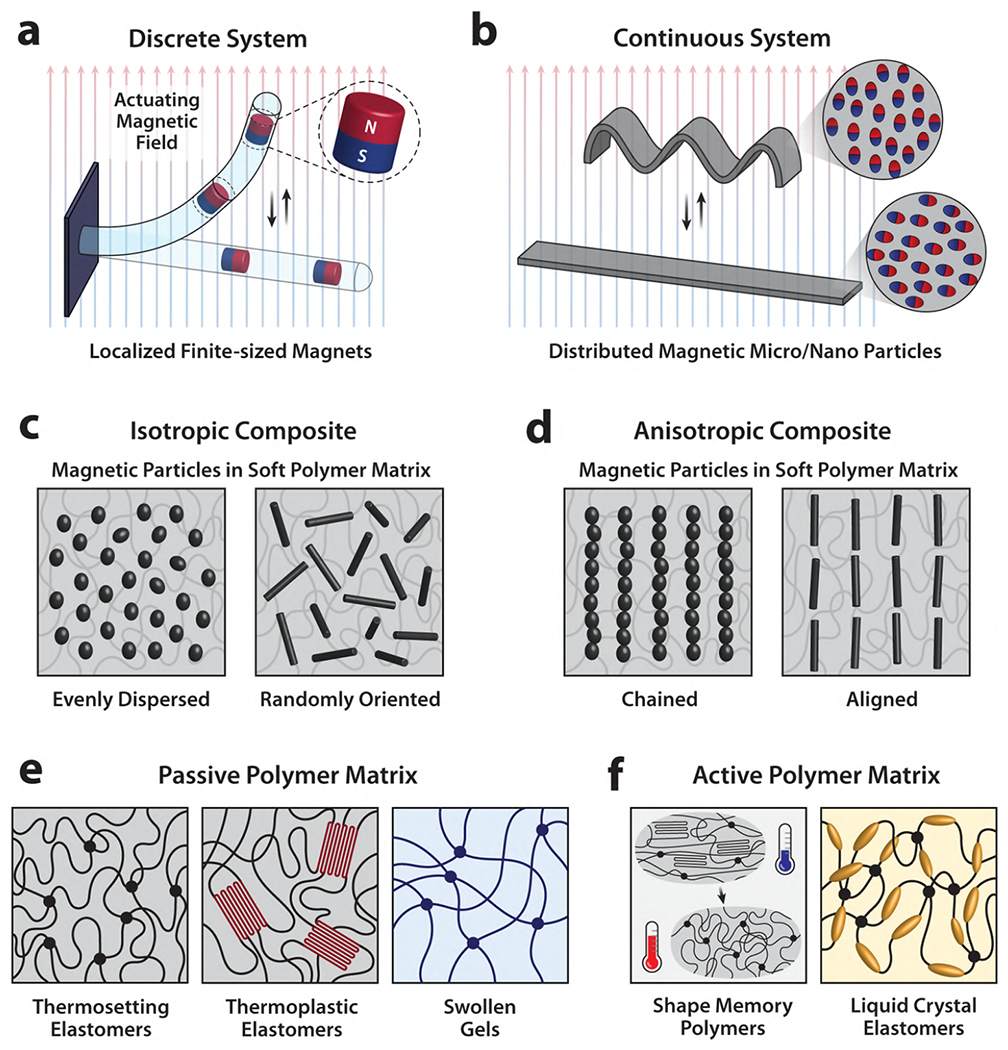
Magnetic soft materials can be classified into either (a) discrete or (b) continuous systems depending on whether the magnetic components are in the form of finite-sized magnets embedded in the flexible structure or micro- or nanoparticles dispersed in the soft polymer matrix. Continuous magnetic soft materials can be further categorized into either (c) mechanically isotropic or (d) anisotropic composites depending on the microscopic structure or arrangement of the magnetic filler particles in the host polymer matrix. The polymeric component of magnetic soft materials can be classified into either (e) passive polymeric materials such as thermosetting or thermoplastic elastomers and swollen gels or (f) active polymeric materials such as shape memory polymers or liquid crystal elastomers depending on whether the polymer matrices themselves are responsive to external stimuli to change their physical properties or produce actuation via deformation.
