Figure 14. Fabrication and magnetic shape-programming methods for magnetic soft materials.
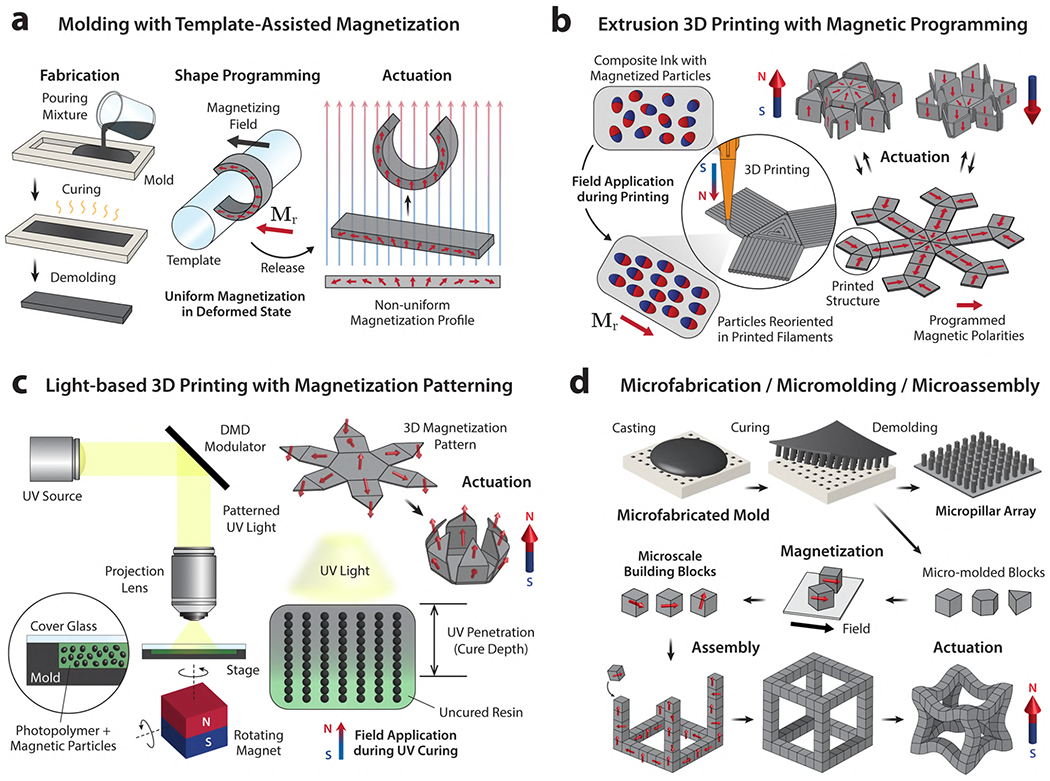
(a) Molding and casting for fabrication and templated-assisted magnetization for shape programming to obtain a nonuniform magnetization profile.166 (b) Extrusion-based 3D printing of magnetic composites containing magnetized particles that can be reoriented by the applied magnetic field during the printing process to program desired magnetization patterns in the printed structure.156 (c) Light-based 3D printing or UV photolithography of magnetic composites based on photocurable resins mixed with magnetic particles, which can be aligned to form chains along the applied field direction during the UV curing process to create desired magnetization patterns in the printed structure.178 (d) Fabrication of micropillar arrays193 or microscale building blocks194 through molding of magnetic soft composites using microfabricated molds. Microscale building blocks based on hard-magnetic composites can be magnetized and assembled into 3D structures capable of programmed shape changes under applied magnetic fields due to the designed magnetization patterns.194
