Figure 5. Torque- and force-driven bending actuation of hard-magnetic soft materials.
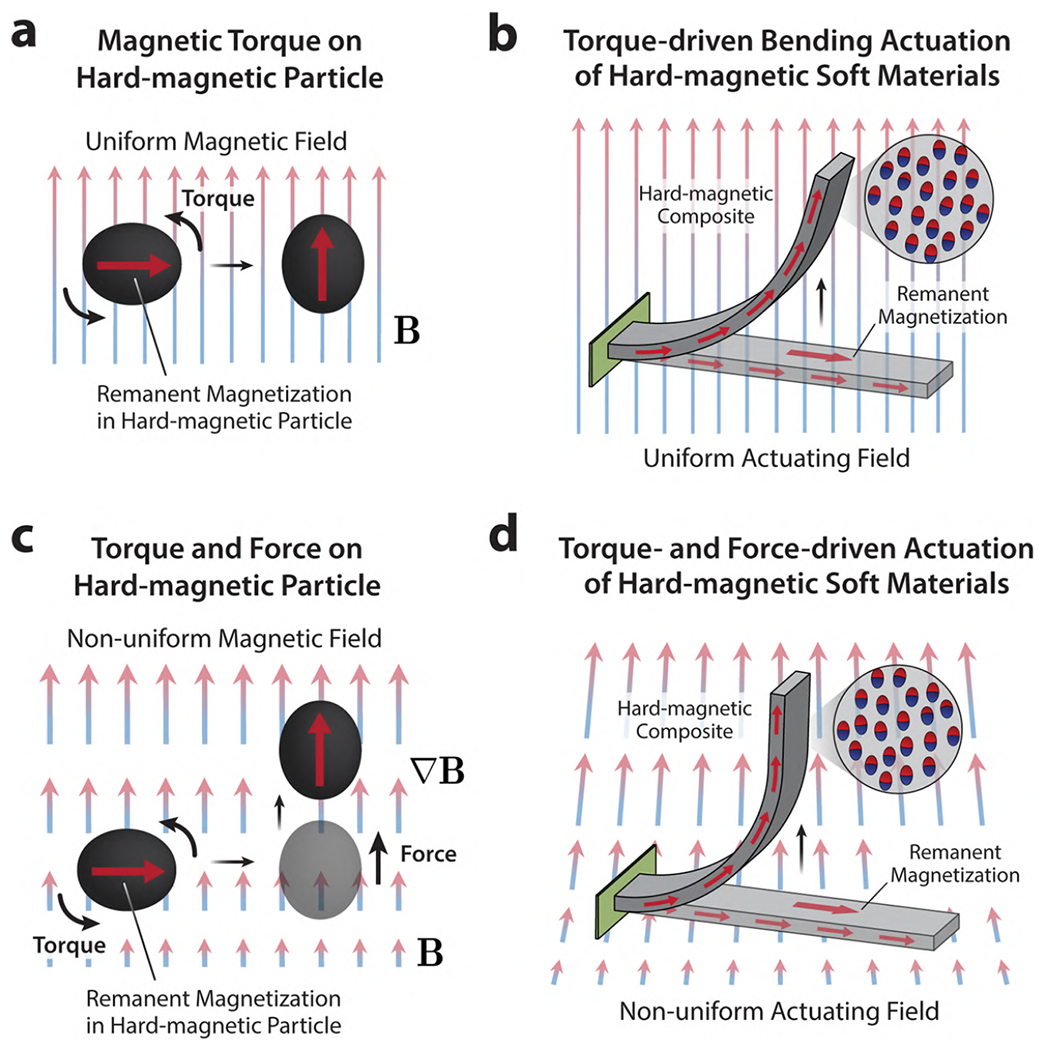
(a) Magnetic torque acting on a magnetized hard-magnetic particle under a spatially uniform magnetic field. (b) Rectangular beam made of a hard-magnetic soft composite that is uniformly magnetized along the length direction and its torque-driven bending actuation under a uniform actuating field that is applied perpendicularly to the beam’s remanent magnetization. (c) Magnetic torque and force acting on a magnetized hard-magnetic particle under a spatially nonuniform magnetic field, in which the particle not only rotates due to the magnetic torque but also moves toward the direction of the increasing field due to the attractive magnetic force. (d) Bending actuation of hard-magnetic soft materials under nonuniform actuating fields is initially driven by the magnetic torque and further supported by the increasing magnetic force as the body deforms to align its remanent magnetization with the applied field.
