Figure. 1.
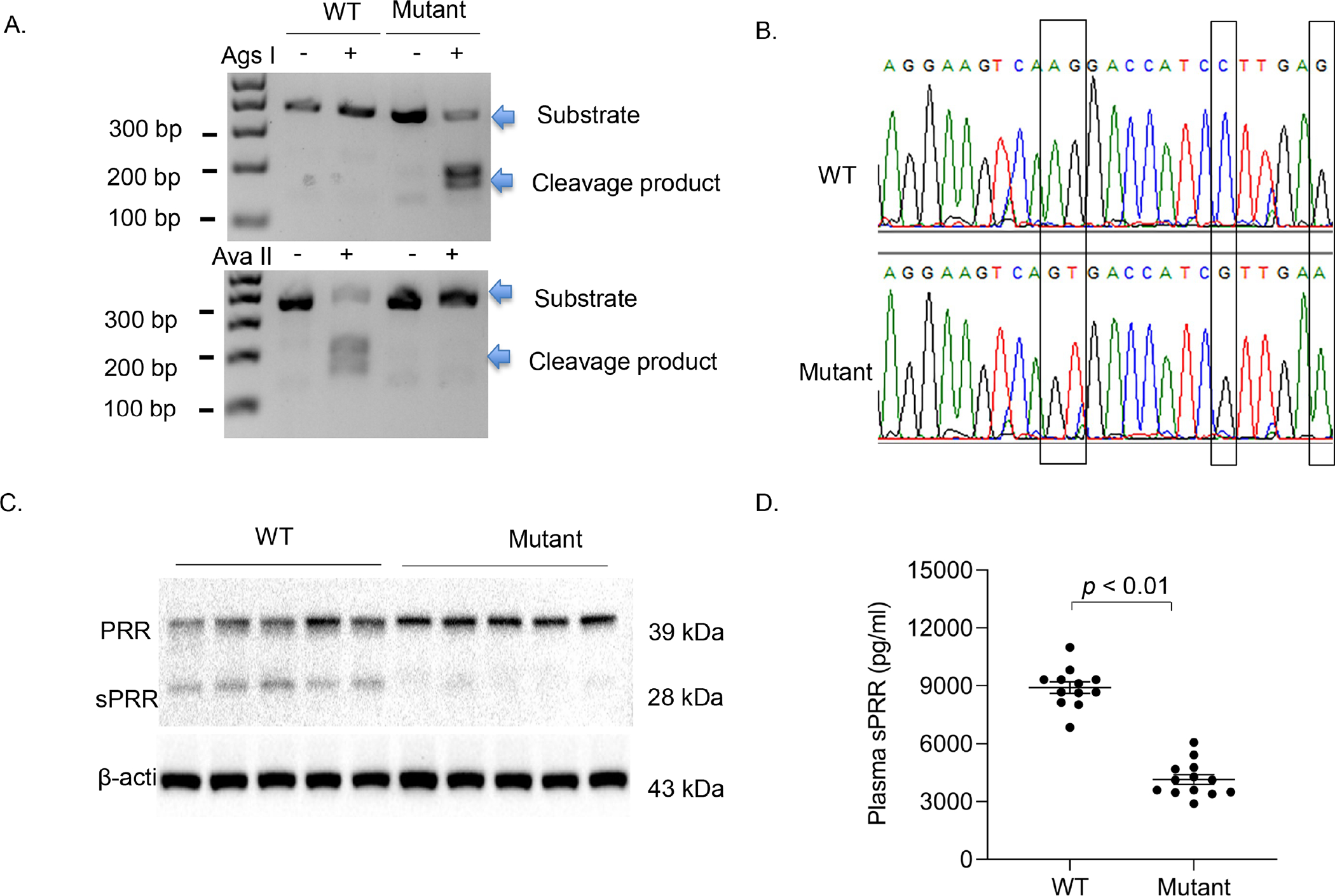
Genotyping of PRRR279V/L282V mice. Genotyping was first performed by PCR using tail DNA. A PCR product of 383 bp spanning the cleavage site was subjected to restriction enzyme digestion followed by DNA electrophoresis (A). The PCR product containing the mutant PRR allele became sensitive to Ags I but not Ava II whereas the product harboring the WT PRR allele remained sensitive to Ava II but not Ags I. (B) DNA sequencing analysis of the PCR products from WT and PRRR279V/L282V mice. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of renal PRR/sPRR expression in the two genotypes (n = 5 per each group). (D) ELISA analysis of plasma sPRR concentrations in the two genotypes (n = 12 per each group). The statistical significance was determined by using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test for 2 comparisons, and the p values were indicated in the figure. Data are mean ± SE. WT, wild-type; Mutant, PRRR279V/L282V.
