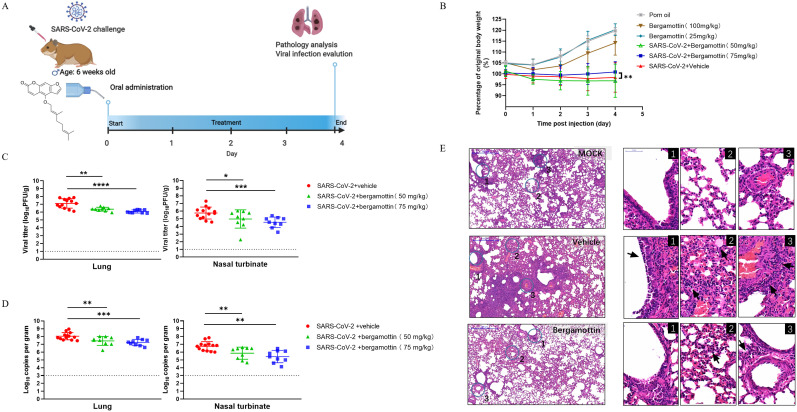
Fig. 5.
Antiviral evaluation of bergamottin in the golden Syrian hamster model. (A) Experimental design of in vivo study: Hamsters were intranasally inoculated with 5 × 104 PFU of SARS-CoV-2, followed by virus challenge where hamsters were orally administrated 50 mg/kg (n = 9) and 75 mg/kg (n = 9) bergamottin doses for four consecutive days. The vehicle group (n = 13) was given corn oil as a control. (B) Daily body weight change curves. (C) Viral yields in the hamster lung tissues and nasal turbinates were harvested at 4 dpi and titrated by plaque assay. (D)Viral loads in the hamster lung tissues and nasal turbinates were subjected to SARS-CoV-2 viral copy detection by RT-qPCR assays. (E) Representative images of H&E-stained lung tissues section from hamsters treated with different groups as indicated. Numbered circled areas are shown in magnified images to the right, illustrating the severity of (1) Bronchiolar epithelium cell death; (2) Destruction of alveoli with massive alveolar space infiltration; (3) Intra-endothelium and perivascular infiltration. Scale bar, 500 μm. Dashed lines indicate the limit of detection. **** P < 0.0001; *** P < 0.001; ** P < 0.01; * P < 0.05.