Table 3.
Estimation of the impact of North–South LCs with enforcement and cooperation on South-North manufacture trade flows, 1995–2014
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ln mijt | ln mijt |
| LC | 0.308** | |
| (0.146) | ||
| LCweak wo strong enforcement or deep cooperation | - | 0.244** |
| (0.076) | ||
| LCcoop with deep cooperation "only" | - | 1.315*** |
| (0.149) | ||
| LCenf with strong enforcement "only" | - | -0.313 |
| (0.209) | ||
| LCenfcoop with strong enforcement and deep cooperation | - | -0.190 |
| (0.137) | ||
| ln (Distanceij) | -1.340*** | -1.334*** |
| (0.080) | (0.031) | |
| Contiguityij | 0.686* | 0.664*** |
| (0.356) | (0.104) | |
| Common Languageij | 0.690*** | 0.653*** |
| (0.111) | (0.039) | |
| Past Colonialij | 1.130*** | 1.147*** |
| (0.178) | (0.051) | |
| Common Colonialij | 0.553*** | 0.489*** |
| (0.180) | (0.066) | |
| Depth of PTAijt | 1.199*** | 0.887*** |
| (0.201) | (0.097) | |
| Sample | South to North | |
| Observations | 23,372 | 23,372 |
| Adj. R-squared | 0.849 | 0.850 |
| importer—year Fixed Effects (it) | Yes | Yes |
| exporter—year Fixed Effects (jt) | Yes | Yes |
OLS estimates. Standard errors in parentheses are clustered at the dyad level; *p < 0.1; **p < 0.05; ***p < 0.01. The reference group is “PTAs with no LCs”. We construct the four variables capturing the four types of LCs as being mutually exclusive, i.e., 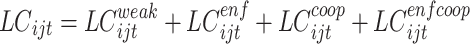
Source: authors' computation
