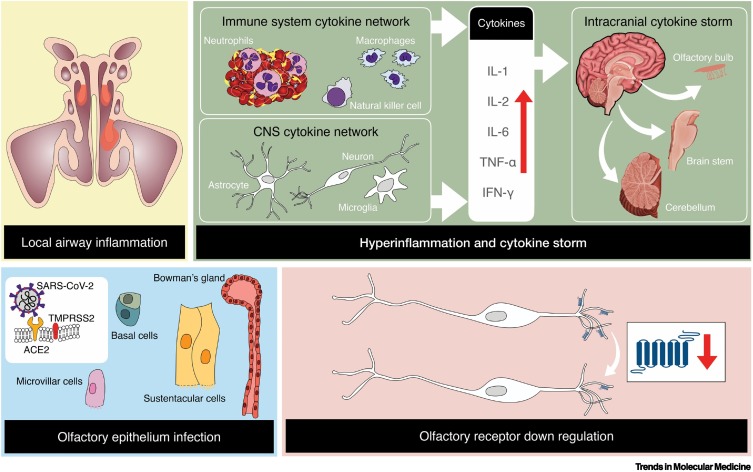
Figure 1.
Suggested mechanisms by which the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus affects the sense of smell.
These include local airway inflammation, particularly in the higher recesses of the nose, infection and damage to specific cell types within the olfactory neuroepithelium, over-reactive immune responses within the brain, and downregulation of olfactory receptor proteins located on the cilia of olfactory receptor cells. As a result of viral infection, macrophages are activated, which in turn releases a multitude of cytokines, with interleukin 6 producing the most inflammation. The listed cytokines are examples and not an inclusive list of cytokines that can influence olfactory functioning. Copyright © 2022 Shima Moein. Abbreviations: ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme II; TMPRSS2, transmembrane protease serine 2.