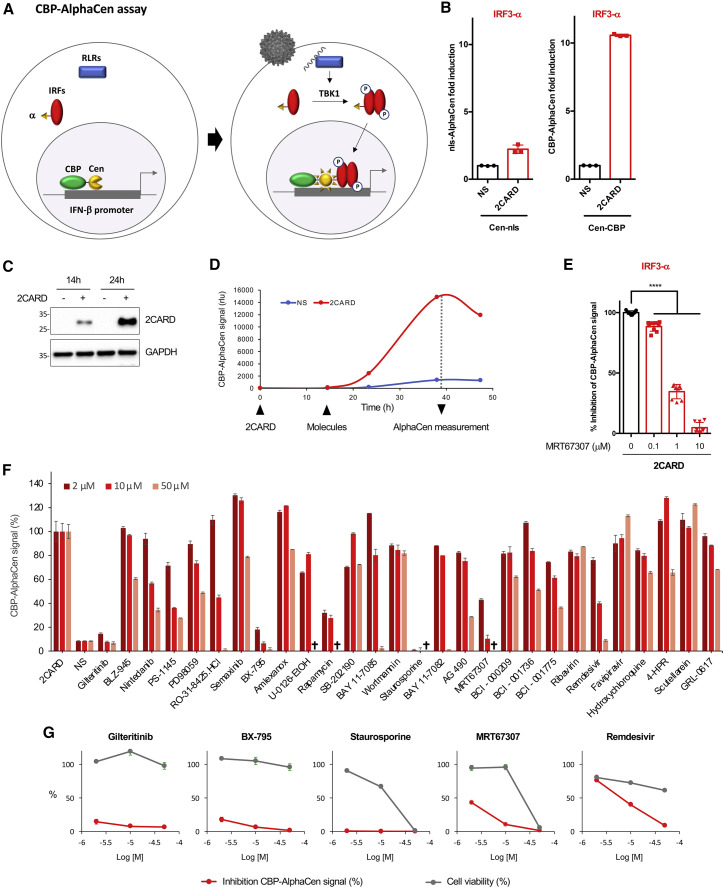
Figure 2.
Measuring activation of IRF3 by IRF3-α/CBP AlphaCen assay allows the screening of immunomodulatory molecules
(A) Schematic representation of the CBP AlphaCen assay, where the Cen fragment is fused to murine CREB-binding protein (CBP).
(B) HEK293T cells were transfected with an empty (NS) or a 2CARD-encoding plasmid, together with IRF3-⍺ and either Cen-nls or Cen-CBP. AlphaCen NLuc signal was measured at 48 hpt. Data correspond to means ± SD of a representative experiment performed in triplicate.
(C) 2CARD expression was assessed by anti-FLAG western blot.
(D) HEK293T cells were transfected with IRF3-α and Cen-CBP together with an empty (NS) or a 2CARD-expressing plasmid. AlphaCen NLuc signal was measured at 14, 24, and 39 hpt. Results are from a single experiment performed in triplicate, representative of two independent experiments.
(E) HEK293T cells were transfected with IRF3-α, Cen-CBP, and 2CARD and treated with MRT67307 at the indicated concentrations at 14 hpt. AlphaCen signal was measured at 24 hpt (39 hpt). Data correspond to means ± SD of three independent experiment performed in triplicate. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, as determined by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test.
(F) A panel of 21 kinase inhibitors and 7 SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors were tested with the IRF3-α/CBP AlphaCen readout. A viability cutoff of 50% was applied to remove cytotoxic compounds (indicated by a cross; see Figure S1C). Results were normalized to the 2CARD-stimulated and untreated control (NS, non-stimulated). Results are the mean of 2 independent screens ± SD.
(G) Graphs show the inhibition of the IRF3-α/CBP AlphaCen signal and cell viability for a selection of drugs.