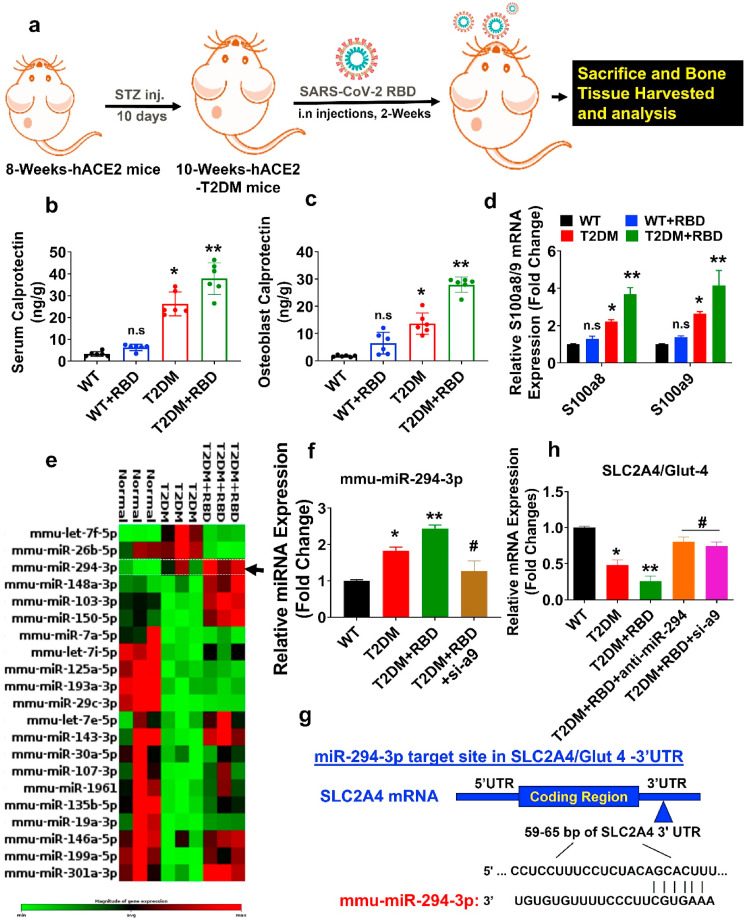
Fig. 1.
SARS-CoV-2 RBD treatment suppresses the Glut4 expression in osteoblast via calprotectin-dependent inflammation in diabetic mice. (a) Ten-week-old female hACE2-T2DM mice were administrated SARS-CoV-2 RBD recombinant protein or vehicle control by the intranasal route and tissue was harvested after 2 weeks. (b–c) ELISA assay of calprotectin level in serum and osteoblast lysate. (d) S100a8/a9 gene expression by qPCR. (e) Heat map of differentially expressed miRNAs in osteoblast by qPCR Array. (f) qPCR validation of miR-294–3p. (g) Targetscan analysis of the miR-294–3p binding sites in 3′-UTR of the SLC2A4/Glut4. (h) qPCR analysis of Glut4 expression. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 6 mice per group. ∗p < 0.05 compared with the WT control, ∗∗p < 0.05 compared with the T2DM, #p ≤ 0.05 compared with the T2DM + RBD.