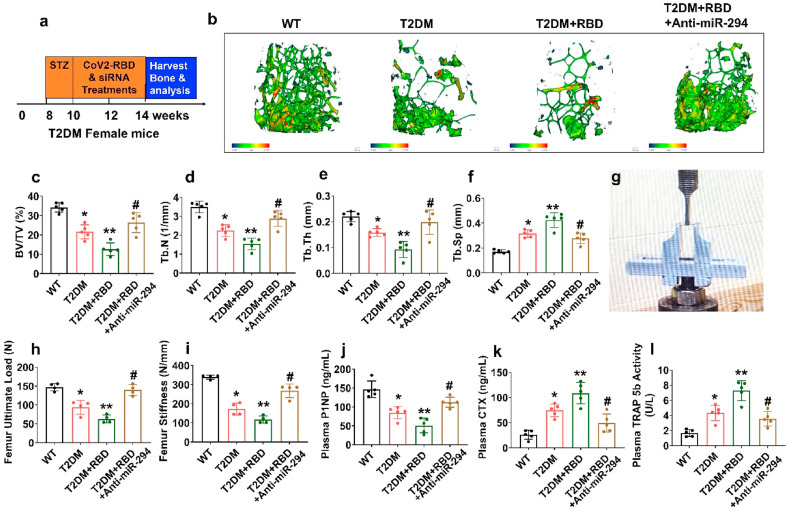
Fig. 4.
SARS-CoV-2 RBD treatment exacerbates pathologic bone loss in T2DM mice. (a) Anti-miR-294 was IV injected into T2DM + RBD mice. The femoral bone samples were harvested, and downstream analyses were performed. (b) MicroCT scan analysis of the distal femur of the experimental mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. (c–f) Trabecular bone phenotype parameters were observed: BMD, BV/TV (%), Tb.N (1/mm), Tb.Th (mm), Tb.Sp (mm). (g–i) Bone mechanical properties such as (Maximum load (N) and stiffness (N/mm)) were analyzed. (j–l) ELISA analysis of P1NP, CTX-I, and TRAP-5b activity was tested. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 5 mice per group. ∗p < 0.05 compared with the WT control, ∗∗p < 0.05 compared with the T2DM, #p ≤ 0.05 compared with the T2DM + RBD.