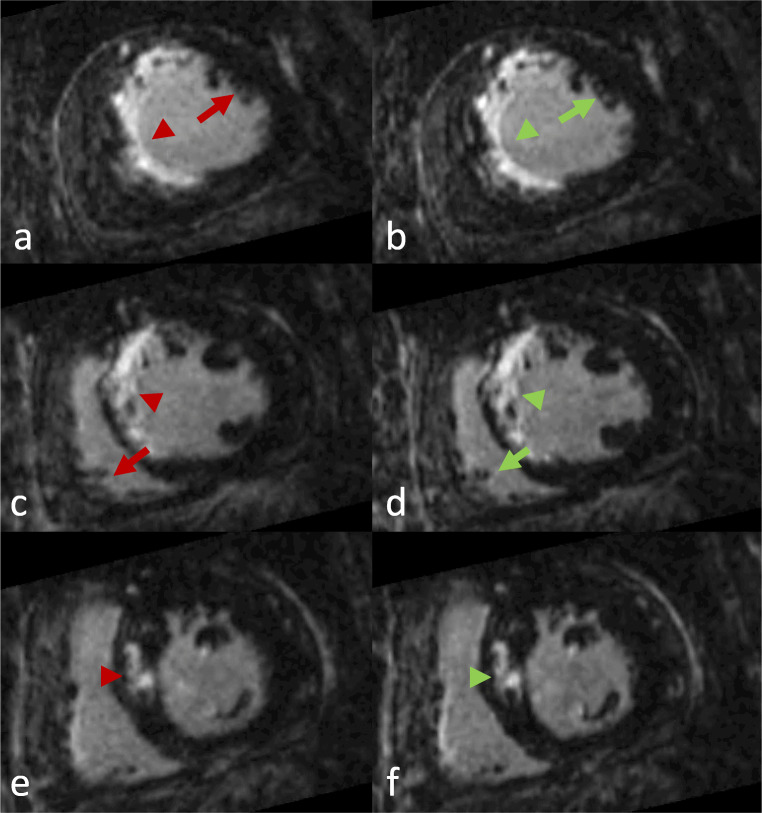
Fig. 4.
Short-axis reformations in a patient with large septal infarction. Left column: TC (translational motion corrected). Right column: NRC (combined translational and non-rigid motion corrected). Axial (a, b) and corresponding midventricular (c, d) and basal (e, f) short-axis reformations. Excellent overall image quality was observed in both datasets. Note, however, the better LGE delimitation (arrowheads) and anatomical details (arrows) in the NRC reconstruction