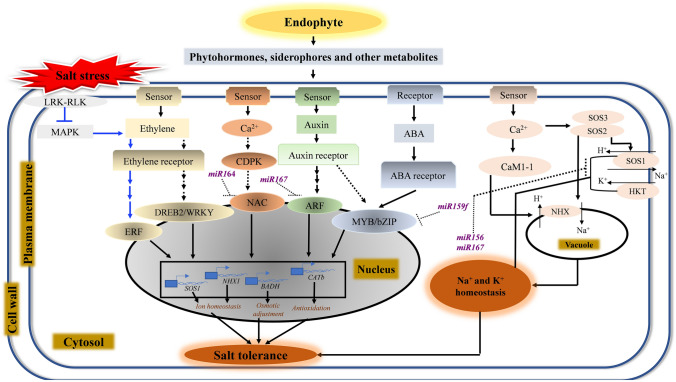
Fig. 1.
Molecular mechanisms regulating endophyte-mediated rice responses to salt stress. The salt stress signal is perceived by various signal transduction sensors transducing the signal along different pathways into the cell. These sensors include membrane-associated kinases, G-protein coupled receptors, glutamate receptor-like channels, calmodulin binding receptors, cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, and Ca2+ channel opening (Jamla and Archak 2019). Endophytes target different components in this signalling system during salt stress in the rice cell. They modulate either phytohormone- such as auxin, ethylene and abscisic acid (ABA) (Liu et al. 2017b; Khan et al. 2020; Sultana et al. 2020), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-, or Ca2+-signalling (through calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPK)) pathways (Jaemsaeng et al. 2018; Chauhan et al. 2019), which transduce the signal into the cell to modulate the expression of transcription factors (TFs) such as ethylene responsive factor (ERF), dehydration-responsive element-binding 2 (DREB2), NAC (NAM, ATAF and CUC), auxin response factor (ARF), and myeloblastosis (MYB). These TFs in turn induce salt-responsive genes (for each case, only representative genes are shown) such as Salt Overly Sensitive 1 (SOS1) and Sodium/Hydrogen eXchanger 1 (NHX1) for ion-homeostasis, Betaine Aldehyde Dehydrogenase (BADH) for osmotic adjustment, and CATALASE b (CATb) for antioxidation (Nautiyal et al. 2013; Ji et al. 2020). They can also target Ca2+-signalling pathway (through calmodulin, CaM1-1) leading to the SOS pathway-mediated ion-homeostasis in the rice cell by activating plasma membrane-bound SOS1 and vacuolar NHX1 (Jaemsaeng et al. 2018) proteins. Endophytes also induce the expression of various salt-responsive miRNAs which can regulate these TFs and structural genes like SOS1 and high-affinity K+ transporter 1 (HKT1) (Kord et al. 2019), supporting the existence of crosstalk between signalling pathways, conferring enhanced salt tolerance in rice. Dashed arrows indicate possible mechanisms. Blue arrows along the pathway from MAPK through ERF indicate endophyte-mediated pathway downregulation