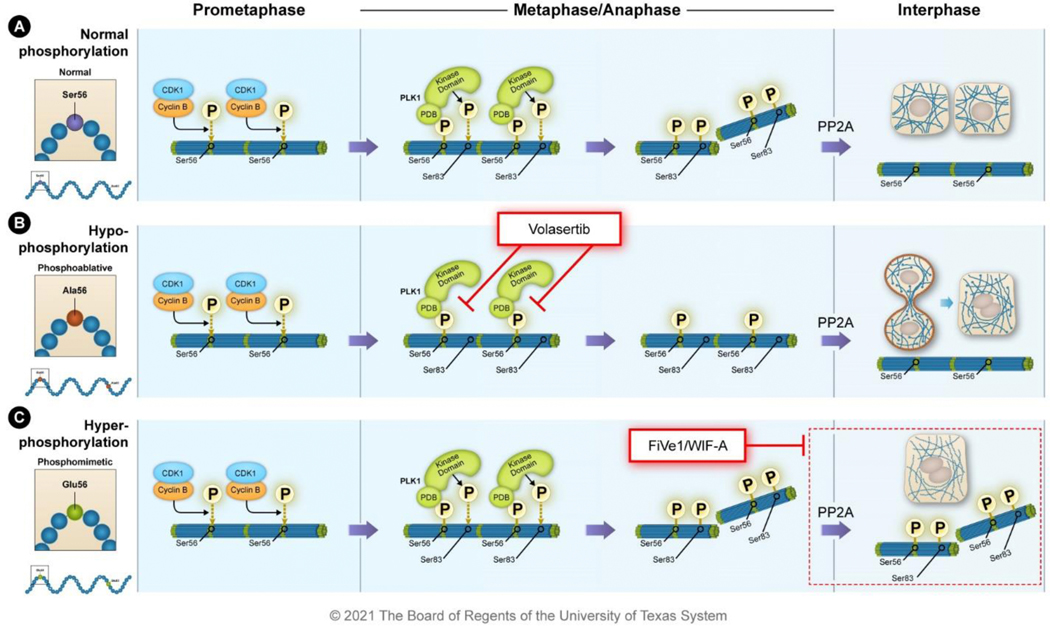
Figure 6. Small-molecule inhibitors have been identified that disrupt vimentin phospho-malleability.
A) During prometaphase, vimentin is phosphorylated at Ser56 by CDK1-cyclin B; this primes subsequent phosphorylation events. The polo-box domain (PDB) of PLK1 binds to the primed phosphorylation site at Ser56 and the kinase domain of PLK1 phosphorylates vimentin Ser83. This leads to the disassembly of the 10-nm filaments into ULFs during metaphase and anaphase. The phosphatase PP2A dephosphorylates vimentin stabilizing the filaments after cytokinesis. B) The PLK1 inhibitor volasertib binds to the ATP pocket of PLK1 preventing phosphorylation of substrates like vimentin. In the presence of volasertib, vimentin remains filamentous during metaphase causing issues during mitosis and cytokinesis that culminate in intermediate filament bridges and polyploidy. C) The small molecules FiVe1 and Withaferin-A (WIF-A) stabilize vimentin phosphorylation causing improper destabilization of vimentin filaments resulting in mitotic catastrophe and polyploidy.