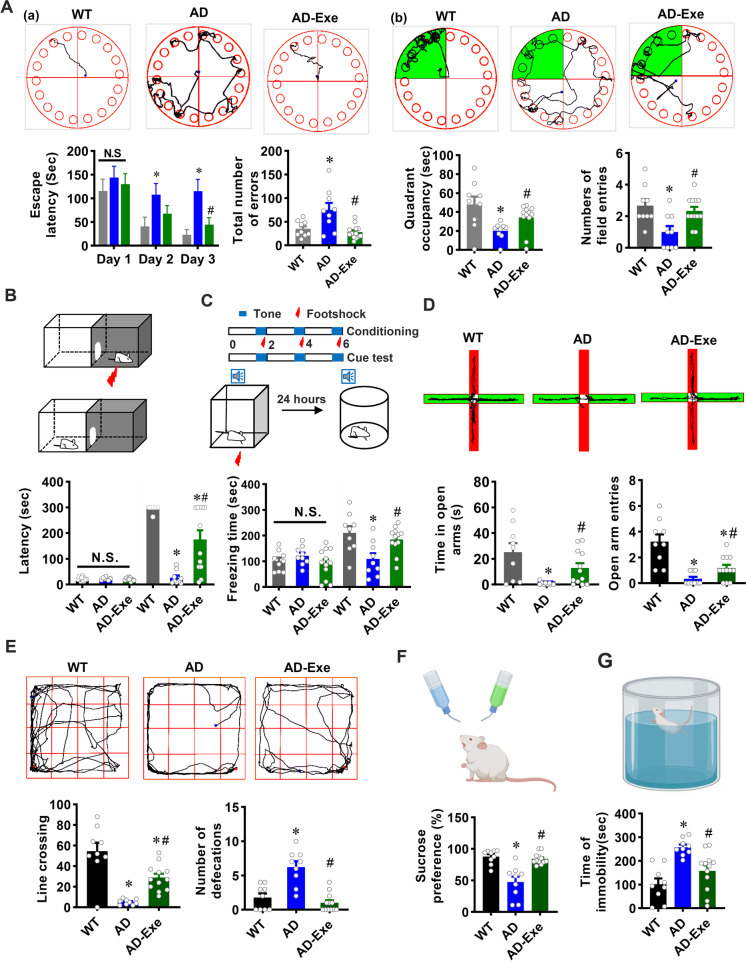
Fig. 2.
Long-term exercise training attenuates memory impairment and anxious-depressive–like behavior of TgF344-AD rats. A The Barnes maze task was performed to measure learning and memory function. (a) Representative tracking plots of rats and results of escape latency and the total number of errors before finding the target box on the training days. (b) Representative tracking plots of rats and results of quadrant occupancy and number of field entries on probe trial day. B The passive avoidance task was conducted to test fear memory. Latency from the lit compartment to the dark compartment. C Cued fear conditioning test was performed to assess associative fear learning and memory. Freezing times were recorded and analyzed. D The elevated plus maze was performed to detect anxiety-like behavior. The time each rat stayed in the open arms and the entries to the open arms were analyzed. E The open field test was performed to assess anxiety-related behavior. Line crossing and defecations in the open field were recorded and analyzed. F The sucrose preference test and G forced swimming test were performed to measure depressive-like behavior. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 9–12). *P < 0.05 versus WT group, #P < 0.05 versus AD group