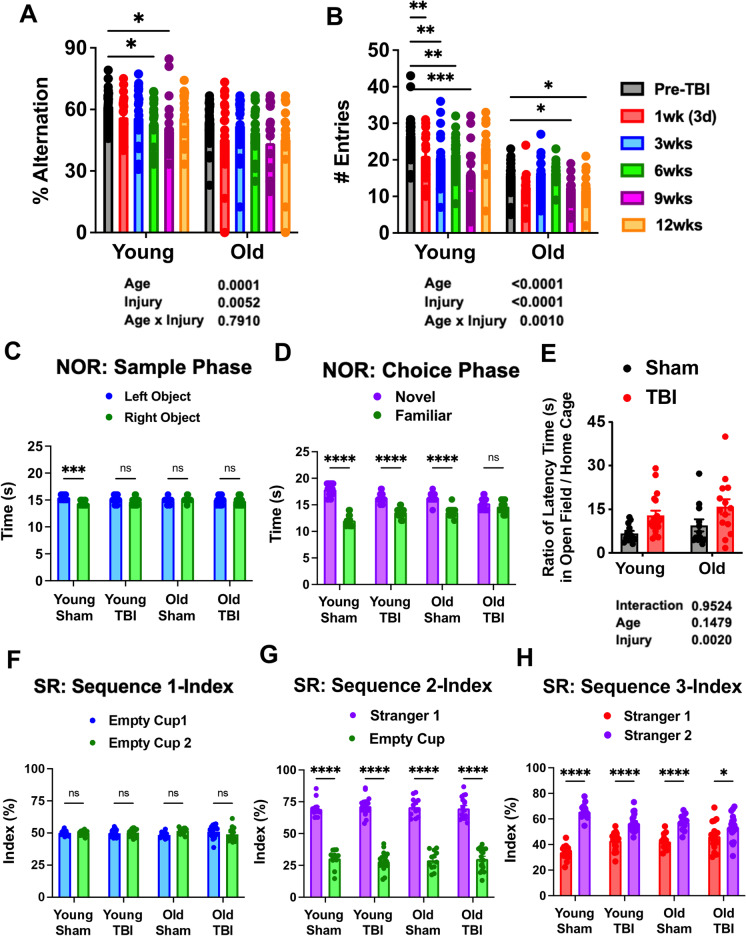
Fig. 2.
Effects of age on long-term cognition, depression, and social behavior. A–B Graph depicting percentage of alternation and total arm entry numbers for young and aged mice in baseline and repeated behavior tests. Significant effects of age and injury could be observed in both parameters observed. C During the sample phase of the NOR task, no differences between groups were seen in exploration time between left and right-side objects. D Graph depicting time spent exploring the novel versus familiar object during the choice phase of the NOR experiment. All groups except Old TBI showed significant preference for novel object over familiar object. E Ratio of latency time to food pellet in open field versus home cage showed injury effects for both age groups, but no aged effects were observed. F–H Graphs depicting preference index of each sequence for the social recognition experiment are shown. N = 13 (young sham), 12 (old sham), 19 (young TBI), and 17 (old TBI). Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05