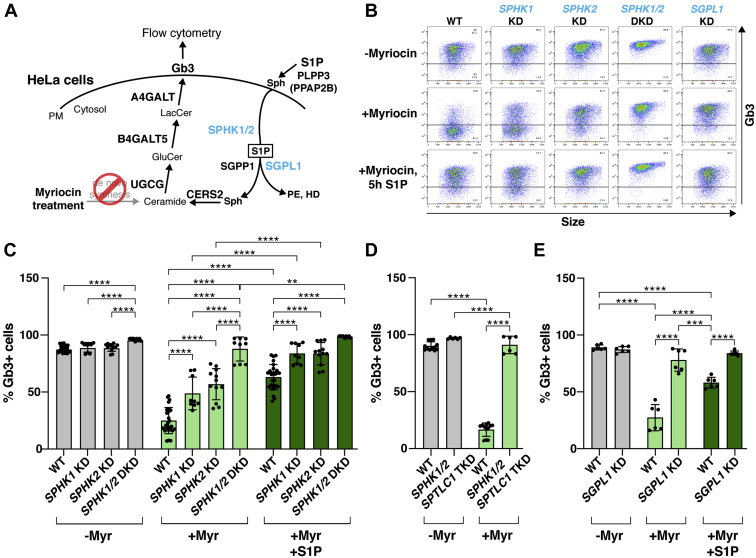
Fig. 5.
SPHK1, SPHK2, or SGPL1 KD elevates Gb3 cell-surface expression. A: Schematic of the potential roles of SPHK1, SPHK2, and SGPL1 in the S1P recycling and degradation pathways. Myriocin treatment inhibits de novo Gb3 synthesis so that Gb3 synthesis via the recycling pathway can be analyzed. B: Representative dot plots of flow cytometry for WT, SPHK1 KD, SPHK2 KD, SPHK1/2 DKD, and SGPL1 KD HeLa cells under three different myriocin/S1P treatment conditions (no myriocin [7 days], 2.5 μM myriocin [7 days], 2.5 μM myriocin [7 days] followed by 3 μM S1P [5 h]). C, D, and E: Quantification of Gb3 cell-surface expression based on flow cytometry data for cells that were not treated with myriocin (gray), treated with myriocin (light green), or treated with myriocin and S1P (dark green). C: Experiments were performed using the SPHK1 KD cell pool, and two cell clones each for SPHK2 KD and SPHK1/2 DKD cells along with WT HeLa cells (WT, n = 24; SPHK1 KD, n = 6; SPHK2 KD, n = 12; SPHK1/2 DKD, n = 9). D: Experiments were performed with two cell clones of SPHK1/2;SPTLC1 TKD and WT HeLa cells (WT, n = 6; SPHK1/2;SPTLC1 TKD, n = 6). E: Experiments were performed using the SGPL1 KD cell pool and WT HeLa cells (WT, n = 6; SGPL1 KD, n = 6). C–E: All experiments for each KD cell line were conducted in triplicate wells for each condition and repeated at least twice. Data represent the mean ± SD. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test; ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. DKD, double knockdown; Gb3, globotriaosylceramide; HD, hexadecenal; KD, knockdown; PE, phosphoethanolamine; PM, plasma membrane; Sph, sphingosine; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; TKD, triple knockdown.