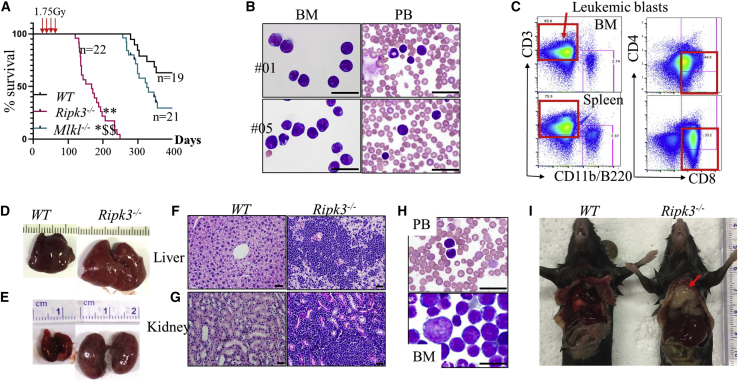
Figure 3.
Inactivation of Ripk3 signaling promotes IR-induced leukemia in mice
WT, Ripk3−/−, and Mlkl−/− mice were X-irradiated at 1.75 Gy weekly × 4. The mice were monitored for leukemia development.
(A–C) Survival curves for the mice were plotted by Kaplan-Meier graphing (A). Leukemia in the mice was diagnosed by examination for leukemic blasts in BM and PB by morphology (B) and flow cytometry (C).
(D–G) Leukemia was further verified by liver and kidney infiltration of leukemic blasts.
(H) Mice transplanted with 1 × 106 leukemic cells from Ripk3−/− mice developed the same types of leukemia as donor mice as demonstrated by morphologic analysis of leukemic blasts in the PB and BM.
(I) Thymoma (indicated by arrow) developed in Ripk3−/− mice but not in WT mice by 200–250 days post-IR. Scale bars in (B), (F), (G), and (H) represent 50 μm.